Extracellular Matrix Influences Gene Expression and Differentiation of Mouse Trophoblast Stem Cells
- PMID: 37463089
- PMCID: PMC10561768
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2022.0290
Extracellular Matrix Influences Gene Expression and Differentiation of Mouse Trophoblast Stem Cells
Abstract
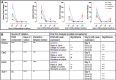
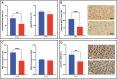
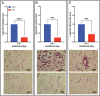
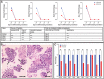
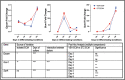
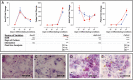
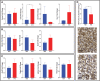
Trophoblast stem (TS) cells were first isolated from the mouse placenta; however, little is known about their maintenance and niche in vivo. TS cells, like other stem cells, have a unique microenvironment in which the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a component. Placental pathology is associated with ECM change. However, how these changes and the individual ECM components impact the maintenance or differentiation of TS cells has not been established. This study identified which ECM component(s) maintain the greatest expression of markers associated with undifferentiated mouse trophoblast stem (mTS) cells and which alter the profile of markers of differentiation based on mRNA analysis. mTS cells cultured on individual ECM components and subsequent quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed that laminin promoted the expression of markers associated with undifferentiated TS cells, fibronectin promoted gene expression associated with syncytiotrophoblast (SynT) layer II cells, and collagen IV promoted the expression of genes associated with differentiated trophoblast. To investigate whether pathological placental ECM influenced the expression of genes associated with different trophoblast subtypes, the mouse model of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced pancreatic β cell ablation and diabetes was used. Female mice administered STZ (blood glucose ≥300 mg/dL) or control (blood glucose ≤150 mg/dL) were mated. Placental pathology at embryonic day (E)14.5 was confirmed with reduced fetal blood space area, reduced expression of the pericyte marker αSMA, and decreased expression of ECM proteins. mTS cells cultured on ECM isolated from STZ placenta were associated with reduced expression of undifferentiated mTS markers and increased expression of genes associated with terminally differentiated trophoblast [Gcm-1 and SynA (SynT) and junctional zone Tpbpa and Prl2c2]. Altogether, these results support the value of using ECM isolated from the placenta as a tool for understanding trophoblast contribution to placental pathology.
Keywords: differentiation; extracellular matrix; mouse; trophoblast; trophoblast stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Tanaka S, Kunath T, Hadjantonakis AK, Nagy A and Rossant J. (1998). Promotion of trophoblast stem cell proliferation by FGF4. Science 282:2072–2075. - PubMed
-
- Okae H, Toh H, Sato T, Hiura H, Takahashi S, Shirane K, Kabayama Y, Suyama M, Sasaki H and Arima T. (2018). Derivation of human trophoblast stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 22:50–63.e6. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Ding W, Wei Q, Shen Z and Wang C. (2012). Dysregulated gene expression of extracellular matrix and adhesion molecules in saphenous vein conduits of hemodialysis patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 144:684–689. - PubMed
-
- Lei T, Hohn HP, Behr R and Denker HW. (2007). Influences of extracellular matrix and of conditioned media on differentiation and invasiveness of trophoblast stem cells. Placenta 28:14–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

