Prediction of Response to Systemic Corticosteroids in Active UC by Microbial Composition-A Prospective Multicenter Study
- PMID: 37463118
- PMCID: PMC10769779
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izad126
Prediction of Response to Systemic Corticosteroids in Active UC by Microbial Composition-A Prospective Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: Corticosteroids are used for induction of remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. However, up to one-third of patients fail to this therapy. We investigated if fecal microbial composition or its metabolic capacity are associated with response to systemic corticosteroids.
Methods: In this prospective, multicenter study, patients with active ulcerative colitis (Lichtiger score ≥4) receiving systemic corticosteroids were eligible. Data were assessed and fecal samples collected before and after 4 weeks of treatment. Patients were divided into responders (decrease of Lichtiger Score ≥50%) and nonresponders. The fecal microbiome was assessed by the 16S rRNA gene marker and analyzed with QIIME 2. Microbial metabolic pathways were predicted using parsimonious flux balance analysis.
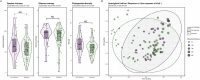
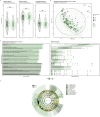
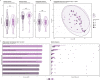
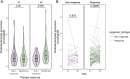
Results: Among 93 included patients, 69 (74%) patients responded to corticosteroids after 4 weeks. At baseline, responders could not be distinguished from nonresponders by microbial diversity and composition, except for a subgroup of biologic-naïve patients. Within 4 weeks of treatment, responders experienced changes in beta diversity with enrichment of ascribed beneficial taxa, including Blautia, Anaerostipes, and Bifidobacterium, as well as an increase in predicted butyrate synthesis. Nonresponders had only minor longitudinal taxonomic changes with a significant increase of Streptococcus salivarius and a microbial composition shifting away from responders.
Conclusion: Baseline microbial diversity and composition seem to be of limited use to predict response to systemic corticosteroids in active ulcerative colitis. Response is longitudinally associated with restoration of microbial composition and its metabolic capacity.
Keywords: butyrate; corticosteroids; microbiome; ulcerative colitis.
© 2023 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are not aware of any affiliations, memberships, funding, or financial holdings that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of this study.
Figures


References
-
- Raine T, Bonovas S, Burisch J, et al. ECCO guidelines on therapeutics in ulcerative colitis: medical treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;16(1):2-17. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Horin S, Har-Noy O, Katsanos KH, et al. Corticosteroids and mesalamine versus corticosteroids for acute severe ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(12):2868-2875.e1. - PubMed
-
- Effenberger M, Reider S, Waschina S, et al. Microbial Butyrate synthesis indicates therapeutic efficacy of azathioprine in IBD patients. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(1):88-98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

