A Rapid and Efficient Method for the Extraction of Histone Proteins
- PMID: 37463329
- PMCID: PMC10408643
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00266
A Rapid and Efficient Method for the Extraction of Histone Proteins
Abstract
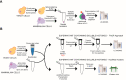
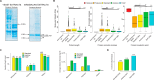
Current protocols used to extract and purify histones are notoriously tedious, especially when using yeast cells. Here, we describe the use of a simple filter-aided sample preparation approach enabling histone extraction from yeast and mammalian cells using acidified ethanol, which not only improves extraction but also inactivates histone-modifying enzymes. We show that our improved method prevents N-terminal clipping of H3, an artifact frequently observed in yeast cells using standard histone extraction protocols. Our method is scalable and provides efficient recovery of histones when extracts are prepared from as few as two million yeast cells. We further demonstrate the application of this approach for the analysis of histone modifications in fungal clinical isolates available in a limited quantity. Compared with standard protocols, our method enables the study of histones and their modifications in a faster, simpler, and more robust manner.
Keywords: chromatin; fungal pathogens; histone-modifying enzymes; histones; post-translational modification; protein extraction; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Accelerated nuclei preparation and methods for analysis of histone modifications in yeast.Methods. 2006 Dec;40(4):296-302. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.06.022. Methods. 2006. PMID: 17101440 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem affinity purification of histones, coupled to mass spectrometry, identifies associated proteins and new sites of post-translational modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Proteomics. 2016 Mar 16;136:183-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Jan 9. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26778144
-
Partial purification of histone H3 proteolytic activity from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2016 Jun;33(6):217-26. doi: 10.1002/yea.3153. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Yeast. 2016. PMID: 26833661
-
Modifying Chromatin by Histone Tail Clipping.J Mol Biol. 2018 Sep 14;430(18 Pt B):3051-3067. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30009770 Review.
-
Histone post-translational modifications regulate transcription and silent chromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2006;(57):127-53. doi: 10.1007/3-540-37633-x_8. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2006. PMID: 16568953 Review.
Cited by
-
HER2; p53 Co-mutated Cancers Show Increased Histone Acetylation and are Sensitive to Neratinib plus Trastuzumab Deruxtecan.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 10:2025.07.06.663368. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.06.663368. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672227 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

