An optimized Nurr1 agonist provides disease-modifying effects in Parkinson's disease models
- PMID: 37463889
- PMCID: PMC10354055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39970-9
An optimized Nurr1 agonist provides disease-modifying effects in Parkinson's disease models
Abstract
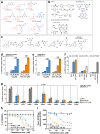
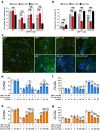
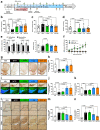
The nuclear receptor, Nurr1, is critical for both the development and maintenance of midbrain dopamine neurons, representing a promising molecular target for Parkinson's disease (PD). We previously identified three Nurr1 agonists (amodiaquine, chloroquine and glafenine) that share an identical chemical scaffold, 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline (4A7C), suggesting a structure-activity relationship. Herein we report a systematic medicinal chemistry search in which over 570 4A7C-derivatives were generated and characterized. Multiple compounds enhance Nurr1's transcriptional activity, leading to identification of an optimized, brain-penetrant agonist, 4A7C-301, that exhibits robust neuroprotective effects in vitro. In addition, 4A7C-301 protects midbrain dopamine neurons in the MPTP-induced male mouse model of PD and improves both motor and non-motor olfactory deficits without dyskinesia-like behaviors. Furthermore, 4A7C-301 significantly ameliorates neuropathological abnormalities and improves motor and olfactory dysfunctions in AAV2-mediated α-synuclein-overexpressing male mouse models. These disease-modifying properties of 4A7C-301 may warrant clinical evaluation of this or analogous compounds for the treatment of patients with PD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W.K., M.T., S.V., S.K.K., R.K., A.T., D.S.R., and K.-S.K. are co-inventors of a pending U.S. utility patent application no. 18/013,155 that is assigned to the McLean Hospital Corporation and the University of Delhi. The patent application no. 18/013,155 describes and claims compounds including SPV-94 (4A7C-301) that are described in this manuscript and methods of using these compounds to treat neurodegenerative diseases. K.-S.K. is a co-founder of NurrOn Pharmaceutical, Inc., which has rights to develop compounds disclosed in this manuscript under a licensing agreement with The McLean Hospital Corporation. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

