Retinol intake is associated with the risk of chronic kidney disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from NHANES
- PMID: 37463986
- PMCID: PMC10354112
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38582-z
Retinol intake is associated with the risk of chronic kidney disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from NHANES
Abstract
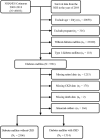
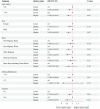
The aim of this study was to investigate the potential association between retinol intake and the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The study included individuals diagnosed with T2DM between 2009 and 2018 from the NHANES database. Demographic and laboratory test data were collected for these individuals, as well as information on CKD diagnosis. Logistic regression models were utilized to estimate the relationship between different retinol intakes and the risk of CKD in patients with T2DM. A total of 3988 patients were included in the study. The mean prevalence of CKD in the T2DM population in the United States from 2009 to 2018 was 36.98 (0.02)%. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed a 26% decrease in the incidence of CKD in individuals with higher retinol intake compared to those with lower retinol intake in T2DM (OR = 0.74; 95% CI 0.56-0.98). Furthermore, an increase in retinol intake per 1-standard deviation (SD) was associated with a 16% decreased risk of the incidence of CKD (OR = 0.84; 95% CI 0.72-0.97). Lower retinol intake is an independent risk factor for the onset of CKD in patients with T2DM, and augmenting moderate quantities of retinol confers potential nephroprotective advantages.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report [Internet]. 2022. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statisticsreport/index.htm.
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas 10th ed. 2021 (https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/. opens in new tab).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

