A prospective double-blinded randomized study on drug-eluting stent implantation into nitrate-induced maximally dilated vessels in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 37464355
- PMCID: PMC10355047
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07497-5
A prospective double-blinded randomized study on drug-eluting stent implantation into nitrate-induced maximally dilated vessels in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been developed using drug-eluting stents (DES); however, stent implantation is associated with concerns of stent thrombosis and target vessel revascularization (TVR). The stent diameter is a critical factor in TVR and clinical events. The nitrate administration in coronary angiography can dilate the reference vessel diameter, enabling accurate vessel size measurement and optimal stent implantation support. This study was designed to evaluate the effect of stent implantation in the maximally dilated coronary artery in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
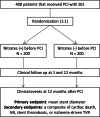
Methods: This prospective double-blinded randomized (1:1) study is designed to compare the efficacy and safety between DES implantation into the nitrate-induced maximally dilated vessels and conventional DES implantation in patients with CAD. A total of 400 patients who underwent PCI with a sirolimus-eluting stent will be enrolled. The primary endpoint is the mean diameter of the deployed stents. Secondary endpoints include cardiac death, myocardial infarction, stent thrombosis, or ischemia-driven TVR 1 year after the procedure.
Discussion: This study will be the first randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of DES implantation on nitrate-induced maximally dilated vessels in patients with CAD.
Trial registration: The trial was registered on 18 June 2021 as Effect of Ultimaster Stents Treated to the Most Dilated Coronary Vessels (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04931784).
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Drug-eluting stent; Nitrates; Randomized controlled trial; Vasodilation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cannon L, Mann JT, Greenberg JD, Spriggs D, et al. Comparison of a polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stent with a bare metal stent in patients with complex coronary artery disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;294(10):1215–1223. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.10.1215. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zahn R, Hamm CW, Schneider S, Richardt G, Kelm M, Levenson B, et al. Coronary stenting with the sirolimus-eluting stent in clinical practice: final results from the prospective multicenter German Cypher Stent Registry. J Interv Cardiol. 2010;23(1):18–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8183.2009.00513.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous