Electroacupuncture improves gout arthritis pain via attenuating ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome overactivation
- PMID: 37464384
- PMCID: PMC10355064
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-023-00800-1
Electroacupuncture improves gout arthritis pain via attenuating ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome overactivation
Abstract
Background: Gout results from disturbed uric acid metabolism, which causes urate crystal deposition in joints and surrounding tissues. Gout pain management is largely limited to colchicine and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Constant usage of these medications leads to severe side effects. We previously showed electroacupuncture (EA) is effective for relieving pain in animal model of gout arthritis. Here we continued to study the mechanisms underlying how EA alleviates gout pain.
Methods: Monosodium urate was injected into ankle joint to establish gout arthritis model in mice. EA or sham EA was applied at ST36 and BL60 acupoints of model animals. Biochemical assays, immunostaining, live cell Ca2+ imaging and behavioral assays were applied.
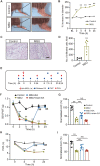
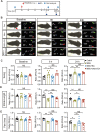
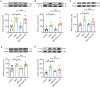
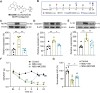
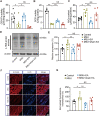
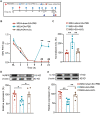
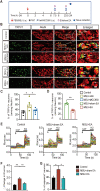
Results: Model mice displayed obvious mechanical allodynia, accompanied with gait impairments. EA attenuated mechanical hypersensitivities and improved gait impairments. EA reduced the overexpression of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling molecules in ankle joints of model animals. EA-induced anti-allodynia, as well as inhibition on NLRP3 inflammasome, were mimicked by antagonizing but abolished by activating NLRP3 inflammasome via pharmacological methods. EA attenuated oxidative stress, an upstream signaling of NLRP3 inflammasome in ankle joints of model mice. Exogenously increasing oxidative stress abolished EA's inhibitory effect on NLRP3 inflammasome and further reversed EA's anti-allodynic effect. EA reduced neutrophil infiltrations in ankle joint synovium, a major mechanism contributing to oxidative stress in gout. Pharmacological blocking NLRP3 inflammasome or EA reduced TRPV1 channel overexpression in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Ca2+ imaging confirmed that EA could reduce functional enhancement in TRPV1 channel in DRG neurons during gout.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that EA reduces gout pain possibly through suppressing ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in inflamed ankle joints and TRPV1 upregulation in sensory neurons, supporting EA as a treatment option for gout pain.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Gout; Inflammasome; Inflammation; Pain; TRPV1.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Eucalyptol alleviates inflammation and pain responses in a mouse model of gout arthritis.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 May;177(9):2042-2057. doi: 10.1111/bph.14967. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31883118 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Mechanical Allodynia of a Rat Model of CRPS-I via Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 25;16:826777. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.826777. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35693886 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Nrf2 antioxidant signaling alleviates gout arthritis pain and inflammation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:115957. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115957. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38042115
-
Natural Products as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Gout.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 16;13:861399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.861399. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Properties of Phytochemicals on NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Gout and Complication.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Jan 31;66(4):765-772. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05113. Epub 2018 Jan 17. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29293001 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemokine CXCL13-CXCR5 signaling in neuroinflammation and pathogenesis of chronic pain and neurological diseases.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Oct 29;29(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00653-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39472796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture treatment of Satoyoshi syndrome: a case report of a rare disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 29;16:1543991. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1543991. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40510477 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Reactive Oxygen Species-Guided Immune Responses in Gouty Arthritis and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 9;14(8):978. doi: 10.3390/biom14080978. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL5 activates CXCR2 in nociceptive sensory neurons to drive joint pain and inflammation in experimental gouty arthritis.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 16;15(1):3263. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47640-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38627393 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy by reducing CCL2-mediated macrophage infiltration in sensory ganglia and sciatic nerve.Chin Med. 2025 Jan 13;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01023-8. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 39806462 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

