Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis
- PMID: 37464413
- PMCID: PMC10353205
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04328-8
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis
Abstract
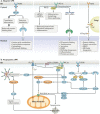
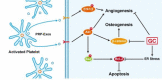
Bone regeneration therapy is clinically important, and targeted regulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is important in regenerative medicine. The processing of proteins in the ER controls cell fate. The accumulation of misfolded and unfolded proteins occurs in pathological states, triggering ER stress. ER stress restores homeostasis through three main mechanisms, including protein kinase-R-like ER kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme 1ɑ (IRE1ɑ) and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), collectively known as the unfolded protein response (UPR). However, the UPR has both adaptive and apoptotic effects. Modulation of ER stress has therapeutic potential for numerous diseases. Repair of bone defects involves both angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Here, we review the effects of ER stress on osteogenesis and angiogenesis, with emphasis on ER stress under high glucose (HG) and inflammatory conditions, and the use of ER stress inducers or inhibitors to regulate osteogenesis and angiogenesis. In addition, we highlight the ability for exosomes to regulate ER stress. Recent advances in the regulation of ER stress mediated osteogenesis and angiogenesis suggest novel therapeutic options for bone defects.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Bone defects; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Exosome; High glucose; Inflammation; Osteogenesis; Unfolded protein response.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systems Biological View of Life-and-Death Decision with Respect to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-The Role of PERK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 5;18(1):58. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010058. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28067773 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by the anti-cancer agent, di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT): Activation of PERK/eIF2α, IRE1α, ATF6 and calmodulin kinase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 1;109:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059255
-
Molecular Basis of Human Diseases and Targeted Therapy Based on Small-Molecule Inhibitors of ER Stress-Induced Signaling Pathways.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(2):118-132. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170306122643. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28266275 Review.
-
Targeting UPR branches, a potential strategy for enhancing efficacy of cancer chemotherapy.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Nov 10;53(11):1417-1427. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab131. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 34664059 Review.
Cited by
-
Paeoniflorin Induces ER Stress-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death by Generating Nox4-Derived ROS under Radiation in Gastric Cancer.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 13;15(24):5092. doi: 10.3390/nu15245092. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38140352 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise Administration of Bone-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticles Encapsulating Valproic Acid and TUDCA Facilitates In Vivo Direct Reprogramming for Osteoporosis Treatment.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Aug;22(6):831-845. doi: 10.1007/s13770-025-00738-5. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40553371
-
(+)-Lipoic acid reduces mitochondrial unfolded protein response and attenuates oxidative stress and aging in an in vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 20;22(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04880-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38245790 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic Acid Accelerates ER Stress-Mediated Inflammation by Increasing PDE4B Expression in Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;196(10):7362-7374. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04859-w. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38523176
-
Functionalized zeolite regulates bone metabolic microenvironment.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Feb 5;31:101558. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101558. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40034985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

