Differential Volume Increase of Endolymphatic Compartments in Ménière's Disease Is Inversely Associated With Membrane Thickness
- PMID: 37464462
- PMCID: PMC10529428
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003960
Differential Volume Increase of Endolymphatic Compartments in Ménière's Disease Is Inversely Associated With Membrane Thickness
Abstract
Objectives: Our aim in this study was to characterize the morphology of the endolymphatic compartment on histopathology in individuals with Ménière's disease (MD) and to determine why hydrops of the saccule is more pronounced than that of other compartments of the inner ear in MD.
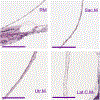
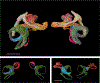
Methods: Temporal bones from 9 patients with idiopathic MD and from 10 individuals without MD/endolymphatic hydrops were examined. The inner ear fluid compartments in normal ears, and ears with MD were three-dimensionally reconstructed and their volume was calculated. The thickness of the membranes of the labyrinth was measured, and both ruptures of the membranes and patency of the utriculoendolymphatic (UEV; Bast's) valve were assessed.
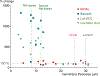
Results: In ears with MD, the saccule and the cochlear duct were most frequently hydropic; the utricle was involved approximately half as frequently. In ears without MD, the Reissner's membrane and the membranous wall of the saccule were thinner than that of the utricle and of the lateral semicircular canal ( p < 0.01). The lateral semicircular canal did not show signs of hydrops. In all ears with MD in which the utricle exceeded the average volume of normals (6 of 12), the UEV was open or there was a rupture in the utricle.
Conclusion: Increases in endolymphatic pressure may cause a primary swelling of the apical cochlear duct and saccule, both of which have relatively thin membranes. Hydrops in the utricle may occur less frequently because of a thicker wall, because of a functioning UEV, and when the saccule has already occupied most of the vestibular perilymphatic space.
Copyright © 2023, Otology & Neurotology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest. B.K.W. is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (K23DC018302), the Hearing Health Foundation, and the Katie and Robert Niehaus Foundation and has a patent US10646723 that is unrelated to the current work. B.B. receives royalties from Oxford University Press.
Figures
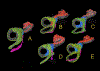
Similar articles
-
Positive pressure therapy for Ménière's disease or syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 10;2015(3):CD008419. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008419.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25756795 Free PMC article.
-
Cochlear, But Not Vestibular, Endolymphatic Hydrops Predominantly Affects Vestibular Function in Patients With Unilateral Menière's Disease.Otol Neurotol. 2025 Sep 1;46(8):965-971. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004511. Otol Neurotol. 2025. PMID: 40788271
-
Limitation of updated MR images on the vestibular hydrops in Meniere's disease.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 May;280(5):2209-2216. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07714-y. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36316577
-
Visualization of Vestibular Aqueduct and Endolymphatic Hydrops in Meniere's Disease With 3D-Real IR.Laryngoscope. 2025 Aug;135(8):2907-2913. doi: 10.1002/lary.32122. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Laryngoscope. 2025. PMID: 40084987
-
Surgical interventions for Ménière's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 24;2(2):CD015249. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015249.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36825750 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hydrops regression after vestibular denervation - longitudinal magnetic resonance study in patients with severe Meniere's disease treated with vestibular neurectomy.Acta Neurol Belg. 2024 Dec;124(6):1923-1934. doi: 10.1007/s13760-024-02605-x. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024. PMID: 39078606 Free PMC article.
-
Meniere's disease: Structural considerations in early cochlea hydrops.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Dec 14;9(6):e70041. doi: 10.1002/lio2.70041. eCollection 2024 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39679170 Free PMC article.
-
Endolymphatic hydrops impairs inner ear uptake and distribution of intratympanically injected gadolinium mixed with dexamethasone in patients with Meniere's disease.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jul;282(7):3513-3521. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09251-w. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39915315
References
-
- Maxwell AK, Ishiyama G, Karnezis S et al. Isolated Saccular Hydrops on High-resolution MRI Is Associated With Full Spectrum Meniere’s Disease. Otol Neurotol 2021;42:876–82. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Escamez JA, Carey J, Chung WH et al. Diagnostic criteria for Meniere’s disease. J Vestib Res 2015;25:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

