Integrated analysis of circRNA, lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA to reveal the ceRNA regulatory network of postnatal skeletal muscle development in Ningxiang pig
- PMID: 37465009
- PMCID: PMC10350537
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1185823
Integrated analysis of circRNA, lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA to reveal the ceRNA regulatory network of postnatal skeletal muscle development in Ningxiang pig
Abstract
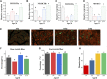
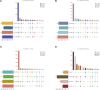
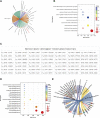
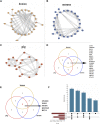
Introduction: The development of skeletal muscle is regulated by regulatory factors of genes and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Methods: The objective of this study was to understand the transformation of muscle fiber type in the longissimus dorsi muscle of male Ningxiang pigs at four different growth stages (30, 90, 150, and 210 days after birth, n = 3) by histological analysis and whole transcriptome sequencing. Additionally, the study investigated the expression patterns of various RNAs involved in muscle fiber transformation and constructed a regulatory network for competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) that includes circular RNA (circRNA)/long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-microRNA (miRNA)-messenger RNA (mRNA). Results: Histomorphology analysis showed that the diameter of muscle fiber reached its maximum at 150 days after birth. The slow muscle fiber transformation showed a pattern of initial decrease followed by an increase. 29,963 circRNAs, 2,683 lncRNAs, 986 miRNAs and 22,411 mRNAs with expression level ≥0 were identified by whole transcriptome sequencing. Furthermore, 642 differentially expressed circRNAs (DEc), 505 differentially expressed lncRNAs (DEl), 316 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmi) and 6,090 differentially expressed mRNAs (DEm) were identified by differential expression analysis. Functions of differentially expressed mRNA were identified by gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). GO enrichment analysis indicates that 40 known genes and 6 new genes are associated with skeletal muscle development. Additionally, KEGG analysis shows that these genes regulate skeletal muscle development via MAPK, FoxO, Hedgehog, PI3K-Akt, Notch, VEGF and other signaling pathways. Through protein-protein interaction (PPI) and transcription factor prediction (TFP), the action mode of skeletal muscle-related genes was explored. PPI analysis showed that there were stable interactions among 19 proteins, meanwhile, TFP analysis predicted 22 transcription factors such as HMG20B, MYF6, MYOD1 and MYOG, and 12 of the 19 interacting proteins were transcription factors. The regulatory network of ceRNA related to skeletal muscle development was constructed based on the correlation of various RNA expression levels and the targeted binding characteristics with miRNA. The regulatory network included 31 DEms, 59 miRNAs, 667 circRNAs and 224 lncRNAs. conclusion: Overall, the study revealed the role of ceRNA regulatory network in the transformation of skeletal muscle fiber types in Ningxiang pigs, which contributes to the understanding of ceRNA regulatory network in Ningxiang pigs during the skeletal muscle development period.
Keywords: Ningxiang pig; ceRNA network; circRNA; lncRNA; skeletal muscle development; whole transcriptome.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Xu, Ai, Wang, Zhang, Li, LiuFu, Liu, Jiang, Gu, Gao and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Whole-transcriptome sequencing revealed the ceRNA regulatory network during the proliferation and differentiation of goose myoblast.Poult Sci. 2024 Nov;103(11):104173. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104173. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39153268 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Targeted Relationships of Novel circRNA803/lncRNA MSTRG.19726-oar-let-7a-CPEB1 ceRNA Networks, Key to Follicle Development in Single-Litter and Multi-Litter Sheep Based on Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5161. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115161. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507971 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Serum Exosome-Derived circRNA-miRNA-TF-mRNA Regulatory Network in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Using Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation in Peripheral Blood-Derived Mononuclear Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;13:899503. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.899503. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35757392 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed non-coding RNAs and their regulatory networks in liver cancer.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 19;9(9):e19223. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19223. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37662778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs and host genes act synergistically in regulating cellular processes and functions in skeletal myogenesis.Gene. 2025 Mar 10;940:149189. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149189. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39724991 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Molecular Mechanism of Skeletal Muscle Development in Ningxiang Pig by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9089. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169089. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201775 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq Identifies Key Genes Affecting Muscle Development in Ningxiang Pigs.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 14;26(6):2634. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062634. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141276 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis revealed differences in gene expression in sheep muscle tissue at different developmental stages.BMC Genom Data. 2024 Jun 7;25(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12863-024-01235-9. BMC Genom Data. 2024. PMID: 38849746 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Regulating Factors of Muscle Fiber Heterogeneity in Livestock: A Review.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;14(15):2225. doi: 10.3390/ani14152225. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of LncRNA-Related ceRNA Networks in Longissimus Dorsi Muscle of Jinfen White Pigs at Different Developmental Stages.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 2;46(1):340-354. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010022. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248324 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

