A radiomics nomogram based on contrast-enhanced CT for preoperative prediction of Lymphovascular invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37465108
- PMCID: PMC10351375
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1208756
A radiomics nomogram based on contrast-enhanced CT for preoperative prediction of Lymphovascular invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background and purpose: To develop a radiomics nomogram based on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) status of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
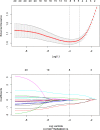
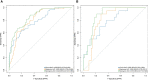
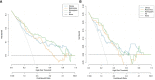
Materials and methods: The clinical and imaging data of 258 patients with ESCC who underwent surgical resection and were confirmed by pathology from June 2017 to December 2021 were retrospectively analyzed.The clinical imaging features and radiomic features were extracted from arterial-phase CECT. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model was used for radiomics feature selection and signature construction. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to develop a radiomics nomogram prediction model. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the performance and clinical effectiveness of the model in preoperative prediction of LVI status.
Results: We constructed a radiomics signature based on eight radiomics features after dimensionality reduction. In the training cohort, the area under the curve (AUC) of radiomics signature was 0.805 (95% CI: 0.740-0.860), and in the validation cohort it was 0.836 (95% CI: 0.735-0.911). There were four predictive factors that made up the individualized nomogram prediction model: radiomic signatures, TNRs, tumor lengths, and tumor thicknesses.The accuracy of the nomogram for LVI prediction in the training and validation cohorts was 0.790 and 0.768, respectively, the specificity was 0.800 and 0.618, and the sensitivity was 0.786 and 0.917, respectively. The Delong test results showed that the AUC value of the nomogram model was significantly higher than that of the clinical model and radiomics model in the training and validation cohort(P<0.05). DCA results showed that the radiomics nomogram model had higher overall benefits than the clinical model and the radiomics model.
Conclusions: This study proposes a radiomics nomogram based on CECT radiomics signature and clinical image features, which is helpful for preoperative individualized prediction of LVI status in ESCC.
Keywords: computed tomography; decision curve analysis; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; lymphovascular invasion; nomogram.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Bai, Huang, Zhang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures



Similar articles
-
Computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of lympho-vascular and perineural invasion in esophageal squamous cell cancer patients: a retrospective cohort study.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Oct 4;24(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00781-w. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39367492 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-Enhanced CT-Based Radiomics Analysis in Predicting Lymphovascular Invasion in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 14;11:644165. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.644165. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34055613 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning model based on enhanced CT radiomics for the preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 23;14:1308317. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1308317. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38549935 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast cancer with dynamic contrast-enhanced-MRI-based radiomics.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Sep;50(3):847-857. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26688. Epub 2019 Feb 17. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30773770
-
Prediction of lymphovascular invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by computed tomography-based radiomics analysis: 2D or 3D ?Cancer Imaging. 2024 Oct 17;24(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00786-5. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39420415 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of lympho-vascular and perineural invasion in esophageal squamous cell cancer patients: a retrospective cohort study.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Oct 4;24(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00781-w. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39367492 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

