IL-17A exacerbates psoriasis in a STAT3 overexpressing mouse model
- PMID: 37465147
- PMCID: PMC10351506
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15727
IL-17A exacerbates psoriasis in a STAT3 overexpressing mouse model
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disease characterized by immunocyte activation, excessive proliferation, and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes. Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) play a crucial role in linking activated keratinocytes and immunocytes during psoriasis development. T helper (Th) 17 cells and secreted interleukin (IL)-17A contribute to its pathogenesis. IL-17A treated STAT3 overexpressing mouse model might serve as an animal model for psoriasis.
Methods: In this study, we established a mouse model of psoriasiform dermatitis by intradermal IL-17A injection in STAT3 overexpressing mice. Transcriptome analyses were performed on the skin of wild type (WT), STAT3, and IL-17A treated STAT3 mice. Bioinformatics-based functional enrichment analysis was conducted to predict biological pathways. Meanwhile, the morphological and pathological features of skin lesions were observed, and the DEGs were verified by qPCR.
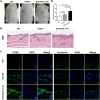
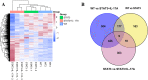
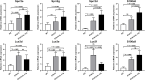
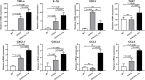
Results: IL-17A treated STAT3 mice skin lesions displayed the pathological features of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis. The DEGs between IL-17A treated STAT3 mice and WT mice were highly consistent with those observed in psoriasis patients, including S100A8, S100A9, Sprr2, and LCE. Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the core DEGs revealed a robust immune response, chemotaxis, and cornified envelope, et al. The major KEGG enrichment pathways included IL-17 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways.
Conclusion: IL-17A exacerbates psoriasis dermatitis in a STAT3 overexpressing mouse.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; IL-17A; Mouse model; Psoriasis; STAT3.
© 2023 Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bergboer JG, Tjabringa GS, Kamsteeg M, van Vlijmen-Willems IM, Rodijk-Olthuis D, Jansen PA, Thuret JY, Narita M, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Zeeuwen PL, Schalkwijk J. Psoriasis risk genes of the late cornified envelope-3 group are distinctly expressed compared with genes of other LCE groups. The American Journal of Pathology. 2011;178(4):1470–1477. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.12.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suarez-Farinas M, Nograles KE, Tian S, Cardinale I, Chimenti S, Krueger JG. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2011;131(3):677–687. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.340. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

