Diagnostics of inflammaging in relation to sarcopenia
- PMID: 37465171
- PMCID: PMC10351926
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1162385
Diagnostics of inflammaging in relation to sarcopenia
Abstract
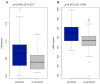
One of the theories about aging focuses on the immune response and relates to the activation of subclinical and chronic inflammation. This study was designed to investigate the relationship between inflammation and sarcopenia and to evaluate the influence of lifestyle on the inflammatory profile. Finally, therapeutic strategies to counteract the pathophysiological effect of skeletal muscle aging were also indicated. One hundred seventy-three individuals aged 71.5 ± 6.8 years were divided into two groups: sarcopenia and probable sarcopenia (n = 39) and no sarcopenia (n = 134). Sarcopenia was assessed according to the algorithm of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in the older adults 2. C-reactive protein (CRP) (p = 0.011) and CRP/albumin ratio (p = 0.030) as well as IL-1β (p = 0.002), cfDNA (p < 0.001) and bilirubin levels (p = 0.002) were significantly higher in the sarcopenia group as opposed to the no sarcopenia group. No significant differences were observed between groups in the concentration of TNFα (p = 0.429) and IL-6 (p = 0.300). An inverse correlation was found between gait speed and cfDNA (rs = -0.234, p < 0.01) and IL-1β (rs = -0.263, p < 0.01). The ROC analysis of cfDNA, CRP, IL-1β and bilirubin ranged from 0.6 to 0.7, which confirms the association between sarcopenia and inflammatory mediators and indicates high clinical usefulness of cfDNA and bilirubin in sarcopenia prediction. We also indicated a link between inflammation and fitness level in the older adult thereby providing evidence that lifestyle exercise should be a key therapeutic strategy in sarcopenia prevention.
Keywords: aging; cytokines; inflammation; lifestyle exercise; sarcopenia; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2023 Morawin, Tylutka, Bielewicz and Zembron-Lacny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory markers are associated with quality of life, physical activity, and gait speed but not sarcopenia in aged men (40-79 years).J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Dec;12(6):1818-1831. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12785. Epub 2021 Sep 15. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 34523822 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Anti-Inflammatory Diet Ingredients and Lifestyle Exercise with Inflammaging.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 21;13(11):3696. doi: 10.3390/nu13113696. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835952 Free PMC article.
-
Serum markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in sarcopenia.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017 Aug;29(4):745-752. doi: 10.1007/s40520-016-0626-2. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 27571781
-
Inflammation and sarcopenia: A focus on circulating inflammatory cytokines.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Oct 15;154:111544. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111544. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 34478826 Review.
-
Inflammaging: The ground for sarcopenia?Exp Gerontol. 2022 Oct 15;168:111931. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.111931. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Exp Gerontol. 2022. PMID: 35985553 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and predictive modeling in a US population with sarcopenia: a propensity score cohort study.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 26;15(1):6953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91437-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40011668 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia attenuates the efficacy of PEGylated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in preventing febrile neutropenia.Support Care Cancer. 2025 Jun 4;33(7):533. doi: 10.1007/s00520-025-09614-3. Support Care Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40464791 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammaging: The Next Challenge-Exploring the Role of Gut Microbiota, Environmental Factors, and Sex Differences.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 1;12(8):1716. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081716. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between albumin-bilirubin score and sarcopenia in middle-aged Americans: a cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 4;12:1606854. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1606854. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40686817 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in self-reported signs related to central sensitization and pressure pain threshold related to knee osteoarthritis and sarcopenia.Eur Geriatr Med. 2024 Oct;15(5):1449-1459. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-01018-6. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Eur Geriatr Med. 2024. PMID: 39012448
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous