Case report: Interstitial pneumonitis after initiation of lamotrigine
- PMID: 37465252
- PMCID: PMC10351415
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1203497
Case report: Interstitial pneumonitis after initiation of lamotrigine
Abstract
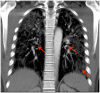
The second-generation anticonvulsant lamotrigine is widely used in the psychiatric field as a mood stabilizer or antidepressant augmentation therapy. Although particularly older anticonvulsants are known for their potential to cause hypersensitivity syndromes, newer antiepileptic drugs do hold a certain risk as well. Presenting a case of a 32-year-old male inpatient of African ethnicity suffering from a primary severe depressive episode in the course of a recurrent major depressive disorder, we report the occurrence of a rapid-onset drug-induced pneumonitis. Herewith, the interstitial pneumonitis occurred after the initiation of 25 mg lamotrigine as an augmentation therapy. Except for the clear temporal correlation between the administration of lamotrigine and the onset of pneumonitis, we did not reveal any further potentially causal diagnostic hints. Importantly, no relevant genetic variations of metabolizing enzymes or drug interactions resulting in lamotrigine overdosage as a potential cause of toxicity were identified. Our experience with a potentially life-threatening adverse drug reaction shortly after the initiation of the largely well-tolerated lamotrigine suggests a potential side effect under the second-generation anticonvulsant although similar adverse events are deemed to be very rare.
Keywords: adverse events; case report; interstitial pneumonitis; lamotrigine (LTG); pulmonary condition.
Copyright © 2023 Watzal, Godbersen, Weidenauer, Willeit, Popper, Treiber, Preiss, Ivkic, Rabl, Fugger, Frey, Kraus, Rujescu and Bartova.
Conflict of interest statement
GF has received consultant/speaker honoraria from Janssen and Angelini. CK has received travel grants and consultant/speaker honoraria from AOP, Roche Austria, Janssen, and LivaNova. Within the last 3 years, DR has received grant/research support from Janssen and Lundbeck; he has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for AC Immune, Janssen, Roche, and Rovi and he has served on speakers bureaus of Janssen and Pharmagenetix, he also received honoraria from Gerot Lannacher, Janssen and Pharmagenetix, and travel support from Angelini and Janssen. Within the last 3 years, LB has received travel grants and consultant/speaker honoraria from Alpine Market Research, Angelini, Biogen, Diagnosia, Dialectica, Janssen, Lundbeck, Market Access Transformation, Medizin Medien Austria, Novartis, Schwabe, and Universimed. RF has received consulting fees from Janssen-Cilag. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kasper SEA, Sachs G, Aichhorn W, Bartova L, Bengesser S, Buchmayer F, et al. . Therapieresistente Depression: Diagnose und Behandlung, Konsensus-Statement. Vienna: Jatros Neurologie & Psychiatrie; (2021).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

