Paroxysmal Ventricular Standstill-A Case Report of all Ps and no QRS in Ventricular Asystole
- PMID: 37465330
- PMCID: PMC10332522
- DOI: 10.21980/J8SS79
Paroxysmal Ventricular Standstill-A Case Report of all Ps and no QRS in Ventricular Asystole
Abstract
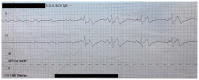
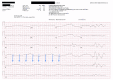
Paroxysmal ventricular standstill, also known as ventricular asystole, is a very rare, often fatal arrhythmia that should be included in the differential of patients presenting with syncope. 1 In this case, a 68-year-old female presented to the emergency department (ED) after sustaining a syncopal episode and subsequent cardiac arrest. On review of cardiac telemetry, she was found to be having episodes of ventricular standstill (VS). Due to her altered mental status, transcutaneous and then transvenous cardiac pacing were initiated. The patient was taken to the catheterization lab where she was found to have no significant coronary blockage, and a permanent pacemaker was placed. The likely culprit was calcium channel blocker toxicity. Paroxysmal ventricular standstill is a non-perfusable arrhythmia that should be rapidly identified. While VS is often a fatal arrhythmia presenting with sudden death, reversible causes should be pursued and treated.2.
Topics: Ventricular standstill, ventricular asystole, heart block, cardiac arrest, emergency pacemaker, transcutaneous pacemaker, transvenous pacemaker, cardiology, Visual EM.
© 2020 Ehsani-Nia, et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidental Findings of Asystole in a Patient With Complaints of Near Syncope: A Case Report on Paroxysmal Ventricular Standstill.Cureus. 2021 Oct 2;13(10):e18438. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18438. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34737906 Free PMC article.
-
Paroxysmal Ventricular Standstill: A Rare Cardiac Manifestation of Syncope.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Jun 17;21:e924381. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.924381. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32598337 Free PMC article.
-
3rd-Degree Atrioventricular Block.J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2022 Apr 15;7(2):O1-O28. doi: 10.21980/J8NP9S. eCollection 2022 Apr. J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 37465444 Free PMC article.
-
Syncope, Epilepsy and Ictal Asystole: A Case Series and Narrative Review.Heart Lung Circ. 2022 Jan;31(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2021.07.003. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Heart Lung Circ. 2022. PMID: 34366218 Review.
-
Pacemakers in patients with familial dysautonomia--a review of experience with 20 patients.Clin Auton Res. 2005 Feb;15(1):15-20. doi: 10.1007/s10286-005-0218-2. Clin Auton Res. 2005. PMID: 15768197 Review.
References
-
- Phibbs B. The Human Heart: A basic guide to heart disease. 2. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007. pp. 111–12.
-
- Petsas A, Pinto R, Kotler M, et al. Sudden and Unexpected Ventricular Standstill in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Chest. 1973;63(3):386–390. - PubMed
-
- Lynch RM, Ballesty L, Maicoo R. “Be still my beating heart”: Ventricular standstill occurring in different age groups. AfJEM. 2014;4(4):e12–e15.
-
- You CF, Chong CF, Wang TL, et al. Unrecognized paroxysmal ventricular standstill masquerading as epilepsy: a Stokes-Adams attack. Epileptic Disord. 2007;9(2):179–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous