SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- PMID: 37465345
- PMCID: PMC10350896
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2023-0752
SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
Abstract
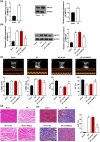
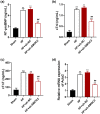
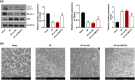
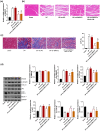
Heart failure (HF) is a major global cause of morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to elucidate the role of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine-related modular calcium-binding protein 2 (SMOC2) in HF development and its underlying mechanism. Using a rat HF model, SMOC2 expression was examined and then knocked down via transfection to assess its impact on cardiac function and damage. The study also evaluated the effects of SMOC2 knockdown on autophagy-related molecules and the transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)/SMAD family member 3 (Smad3) signaling pathway. Intraperitoneal injection of the TGF-β agonist (SRI-011381) into the HF rat model was performed to explore the SMOC2-TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway relationship. SMOC2 expression was elevated in HF rats, while its downregulation improved cardiac function and damage. SMOC2 knockdown reversed alterations in the LC3-II/I ratio, Beclin-1, and p62 levels in HF rats. Through transmission electron microscope, we observed that SMOC2 knockdown restored autophagosome levels. Furthermore, SMOC2 downregulation inhibited the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway, which was counteracted by SRI-011381. In conclusion, SMOC2 knockdown inhibits HF development by modulating TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling-mediated autophagy, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target for HF.
Keywords: SMOC2; TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway; autophagy; heart failure.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Huang S, Wei Q, Zhi X, Wang J, Zhang Z. Application value of serum sST2 in diagnosis and prognosis of heart failure. Sheng wu Gong Cheng xue bao. Chin J Biotechnol. 2020;36(9):1713–22. - PubMed
-
- Dobre D, Borer JS, Fox K, Swedberg K, Adams KF, Cleland JG, et al. Heart rate: a prognostic factor and therapeutic target in chronic heart failure. The distinct roles of drugs with heart rate-lowering properties. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16(1):76–85. - PubMed
-
- Shah SJ, Feldman T, Ricciardi MJ, Kahwash R, Lilly S, Litwin S, et al. One-year safety and clinical outcomes of a transcatheter interatrial shunt device for the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the reduce elevated left atrial pressure in patients with heart failure (REDUCE LAP-HF I) trial: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2018;3(10):968–77. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
