LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- PMID: 37465354
- PMCID: PMC10350895
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2023-0710
LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
Abstract
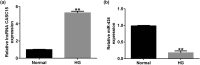
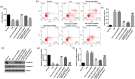
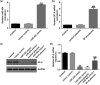
Study has demonstrated the abnormal expression and role of lncRNA CASC15 in diabetes patients with chronic renal failure. However, its role in diabetes nephropathy (DN) is still unclear. This study aimed to investigate the potential mechanism and role of lncRNA CASC15 in DN. The relationship between miR-424 and CASC15/SP-A was predicted by Starbase software and verified by luciferase reporter assay. HK-2 cells were treated with 25 mM glucose (HG) for 24 h to establish DN cell model. MTT and flow cytometry analysis were carried out to test cell proliferation and apoptosis. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers were analyzed by RT-qPCR and western blot assay. We proved that CASC15 could interact with miR-424, and SP-A was a target of miR-424. HG-treatment significantly enhanced lncRNA CASC15 level and decreased miR-424 level in HK-2 cells. LncRNA CASC15-siRNA significantly improved cell viability, repressed apoptosis, promoted E-cadherin expression, and inhibited N-cadherin expression in HG-treated HK-2 cells, and these effects were reversed by miR-424 inhibitor. SP-A was highly expressed in HG-treated HK-2 cells. The biological effects of miR-424 mimic on HG-treated HK-2 cells were reversed by SP-A-plasmid. In conclusion, lncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieved HG-induced HK-2 cell injury and EMT through miR-424/SP-A axis.
Keywords: DN; HK-2 cells; LncRNA CASC15; MiRNA-424; SP-A.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

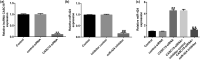


Similar articles
-
Circ_0000064 promotes high glucose-induced renal tubular epithelial cells injury to facilitate diabetic nephropathy progression through miR-532-3p/ROCK1 axis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Mar 15;22(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00968-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35291991 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthohumol ameliorates diabetic kidney disease through suppression of renal fibrosis by regulating SNHG10/miR-378b.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 27;16:1532517. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532517. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40495890 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and fibrogenesis by regulating the miR-216a-5p/BMP7 axis in diabetic nephropathy.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020 Apr 9;53(4):e9288. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20209288. eCollection 2020. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. Retraction in: Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 May 15;56:e9288retraction. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e9288retraction. PMID: 32294702 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
LncRNA-ATB participates in the regulation of calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal injury by sponging the miR-200 family.Mol Med. 2021 Nov 4;27(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00403-2. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34736391 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Targeting the miR-2355-3p/IL6ST Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 29;12:647650. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647650. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995063 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variants and Haplotype Structures in the CASC Gene Family to Predict Cancer Risk: A Bioinformatics Study.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 5;7(12):e70228. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70228. eCollection 2024 Dec. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39640032 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of action of miR-483-3p in mediating the effects of IGF-1 on human renal tubular epithelial cells induced by high glucose.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 7;14(1):15635. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66433-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38972889 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and potential pharmacological mechanism of Astragalus-Salvia miltiorrhiza combination in diabetic nephropathy: integrating meta-analysis, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2466116. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2466116. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40015687 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
