Sparse Independence Component Analysis for Competitive Endogenous RNA Co-Module Identification in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 37465460
- PMCID: PMC10351610
- DOI: 10.1109/JTEHM.2023.3283519
Sparse Independence Component Analysis for Competitive Endogenous RNA Co-Module Identification in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to be associated with the pathogenesis of different kinds of diseases and play important roles in various biological processes. Although numerous lncRNAs have been found, the functions of most lncRNAs and physiological/pathological significance are still in its infancy. Meanwhile, their expression patterns and regulation mechanisms are also far from being fully understood.
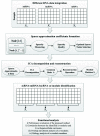
Methods: In order to reveal functional lncRNAs and identify the key lncRNAs, we develop a new sparse independence component analysis (ICA) method to identify lncRNA-mRNA-miRNA expression co-modules based on the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) theory using the sample-matched lncRNA, mRNA and miRNA expression profiles. The expression data of the three RNA combined together is approximated sparsely to obtain the corresponding sparsity coefficient, and then it is decomposed by using ICA constraint optimization to obtain the common basis and modules. Subsequently, affine propagation clustering is used to perform cluster analysis on the common basis under multiple running conditions to obtain the co-modules for the selection of different RNA elements.
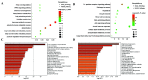
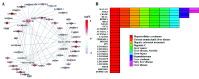
Results: We applied sparse ICA to Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (LIHC) dataset and the experiment results demonstrate that the proposed sparse ICA method can effectively discover biologically functional expression common modules.
Conclusion: It may provide insights into the function of lncRNAs and molecular mechanism of LIHC. Clinical and Translational Impact Statement-The results on LIHC dataset demonstrate that the proposed sparse ICA method can effectively discover biologically functional expression common modules, which may provide insights into the function of IncRNAs and molecular mechanism of LIHC.
Keywords: LIHC; Sparse ICA; ceRNA; co-expression modules; lncRNA.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. For more information, see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying lncRNA and mRNA Co-Expression Modules from Matched Expression Data in Ovarian Cancer.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2020 Mar-Apr;17(2):623-634. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2864129. Epub 2018 Aug 7. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30106686
-
CeModule: an integrative framework for discovering regulatory patterns from genomic data in cancer.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb 7;20(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2654-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30732558 Free PMC article.
-
Excavating novel diagnostic and prognostic long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and gene co-expression networks.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12821-12838. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2003925. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34898376 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
The Role of Long Non-Coding RNA and microRNA Networks in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10630. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910630. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the oncogenic role of LINC00504 and its interaction with miR-545-3p and ARIHI in hepatocellular carcinoma: novel insights for molecular therapy.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 17;16(1):548. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02328-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40244538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jathar S., Kumar V., Srivastava J., and Tripathi V., “Technological developments in lncRNA biology,” Long Non Coding RNA Biol., vol. 1008, pp. 283–323, Aug. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Slaby O., Laga R., and Sedlacek O., “Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer,” Biochem. J., vol. 474, no. 24, pp. 4219–4251, Dec. 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

