Use of an Autologous Heterogenous Skin Construct in the Treatment of Intractable Late-Effect Radiation Wounds: Case Series
- PMID: 37465475
- PMCID: PMC10350875
Use of an Autologous Heterogenous Skin Construct in the Treatment of Intractable Late-Effect Radiation Wounds: Case Series
Abstract
Background: Late-effect radiation-induced wounds represent a particularly difficult category of wounds to manage and treat. Fibrosis, impaired cellular activity, ischemia, and wound chronicity all work to impair healing, and this becomes more pronounced when defects are large or when avascular structures such as bone are exposed. Effective treatment options for this type of wound are limited. Thorough excision of irradiated tissue followed by distal pedicled or free flap closure is the most successful; however, this often requires multiple-stage surgeries and prolonged hospitalization and is associated with significant donor site morbidity. This is complicated further when wounds are large or in difficult locations, when surgery is not appropriate, or when there is limited access to surgeons with the appropriate experience/skill to perform such procedures.
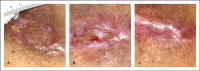
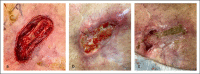
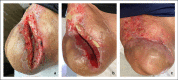
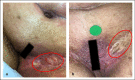
Methods: This case series describes the use of an autologous heterogenous skin construct (AHSC) made from a small full-thickness sample of the patient's healthy skin. Three patients with intractable late-effect radiation wounds were treated with AHSC. Case 1 describes an abdominal wound with tunneling of 7.5 cm to the pubic symphysis, which had been treated for known osteomyelitis, and a shallower full-thickness groin wound. Case 2 describes a right scapular wound with exposed bone, which had failed flap closure. Case 3 describes a right thigh wound in a patient who had been treated for sarcoma with extensive radiation therapy. This eventually resulted in an above-the-knee amputation, which failed to heal, and full exposure of the distal end of the resected femur. All wounds had been present for greater than 10 months.
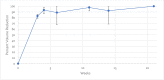
Results: Mean percent volume reduction was 83% (±2.7) at 3 weeks and 92.9% (±4.7) at 4 weeks. The tunneled abdominal wound decreased in depth from 7.5 cm to 1.2 cm in 3 weeks. Complete closure was achieved at 11 weeks for the abdominal and groin wounds (patient 1) and at 16 weeks for the thigh wound (patient 3). The scapular wound volume of patient 2 had decreased by 91.8% at week 4 but was not fully restored until week 21. Mean time to closure was 16.1 (±4.7) weeks.
Conclusions: AHSC was effective in covering exposed bone, improving wound bed vascularity, filling in significant wound depth, and achieving complete wound closure with one application in patients with intractable late-effect radiation wounds.
Keywords: AHSC; Autologous; Chronic Wound; Radiation Injury; Regenerative Medicine; Soft Tissue Radio Necrosis; Soft Tissue Reconstruction; Wound Healing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment of Stage 4 Pressure Injuries With Autologous Heterogenous Skin Construct: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.Eplasty. 2023 May 3;23:e26. eCollection 2023. Eplasty. 2023. PMID: 37234455 Free PMC article.
-
The use of tensor fascia lata pedicled flap in reconstructing full thickness abdominal wall defects and groin defects following tumor ablation.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2005 Sep;17(3):139-48. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2005. PMID: 16799651
-
[Clinical application of lobulated transplantation of free anterolateral thigh perforator flap in the treatment of electric burns of limbs].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 20;35(11):790-797. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.11.005. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31775467 Chinese.
-
Regenerative Medicine: Charting a New Course in Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016 Jul 1;5(7):314-328. doi: 10.1089/wound.2015.0663. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016. PMID: 27366592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-Induced Tissue Damage: Clinical Consequences and Current Treatment Options.Semin Plast Surg. 2021 Aug;35(3):181-188. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1731464. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Semin Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34526866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Majeed H, Gupta V. Adverse Effects Of Radiation Therapy. StatPearls. Published online 2022. Accessed March 28, 2022. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33085406/ - PubMed
-
- Bryant AK, Banegas MP, Martinez ME, Mell LK, Murphy JD. Trends in Radiation Therapy among Cancer Survivors in the United States, 2000-2030. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 2017;26(6):963-970. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-1023 - DOI - PubMed
-
- DiCarlo AL, Bandremer AC, Hollingsworth BA, et al. . Cutaneous Radiation Injuries: Models, Assessment and Treatments. Radiat Res. 2020;194(3):315. doi:10.1667/RADE-20-00120.110.1667/RADE-20-00120.1 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Devalia HL, Mansfield L. Radiotherapy and wound healing. Int Wound J. 2008;5(1):40-44. doi:10.1111/J.1742-481X.2007.00351.X10.1111/j.1742-481X.2007.00351.x - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dormand EL, Banwell PE, Goodacre TEE. Radiotherapy and wound healing. Int Wound J. 2005;2(2):112-127. doi:10.1111/J.1742-4801.2005.00079.X10.1111/j.1742-4801.2005.00079.x - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
