Two-step strategy-conjunctival flap covering surgery combined with secondary deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty for the treatment of high-risk fungal keratitis
- PMID: 37465508
- PMCID: PMC10333253
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2023.07.10
Two-step strategy-conjunctival flap covering surgery combined with secondary deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty for the treatment of high-risk fungal keratitis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether the two-step strategy [conjunctival flap covering surgery (CFCS) combined with secondary deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK)] is effective for patients with high-risk fungal keratitis (FK).
Methods: In this noncomparative, retrospective case series, 10 subjects (6 males, 4 females) with a mean age of 56.5±7.1 (range 47-72)y with high-risk FK undergone the two-step strategy were included. Reported outcome measures were healing of the corneal ulcer, recurrence of FK, reject reaction, improvement in best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and relevant complications.
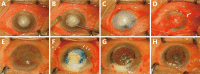
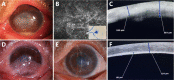
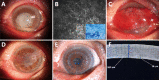
Results: The average diameter of corneal infiltrates was 7.50±0.39 mm, ranging from 6.94 to 8.13 mm. The mean depth of corneal infiltrates was 422.4±77.1 µm, ranging from 350 to 535 µm. The mean corneal thickness was 597.4±117.3 µm, ranging from 458 to 851 µm. Hypopyon and endothelial plaques were presented in all patients. The period between the two steps was 3.65±0.9 (ranging from 3 to 5)mo. The graft diameter was 7.75±0.39 mm. At the last follow-up (average 9.25±3.39, ranging from 5.5 to 17mo), no fungal recurrence or graft rejection appeared, and all patients showed improvement of BCVA. One patient suffered from liver function impairment due to oral voriconazole for 4wk and recovered spontaneously after 1wk of drug withdrawal.
Conclusion: The two-step strategy is safe and effective in the treatment of high-risk FK by transforming intentional therapeutic penetrating keratoplasty during acute infection to later optical DALK. It is a practical strategy, especially in areas lacking fresh donor corneas and eye bank services.
Keywords: conjunctival flap; deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty; fungal keratitis; high-risk; two-step strategy.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
References
-
- Brown L, Leck AK, Gichangi M, Burton MJ, Denning DW. The global incidence and diagnosis of fungal keratitis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(3):e49–e57. - PubMed
-
- Niu LZ, Liu X, Ma ZM, Yin Y, Sun LX, Yang LF, Zheng YJ. Fungal keratitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and prevention. Microb Pathog. 2020;138:103802. - PubMed
-
- Sharma N, Bagga B, Singhal D, Nagpal R, Kate A, Saluja G, Maharana PK. Fungal keratitis: a review of clinical presentations, treatment strategies and outcomes. Ocul Surf. 2022;24:22–30. - PubMed
-
- Prajna NV, Krishnan T, Rajaraman R, Patel S, Srinivasan M, Das M, Ray KJ, O'Brien KS, Oldenburg CE, McLeod SD, Zegans ME, Porco TC, Acharya NR, Lietman TM, Rose-Nussbaumer J. Effect of oral voriconazole on fungal keratitis in the mycotic ulcer treatment trial II (MUTT II) JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(12):1365. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prajna NV, Krishnan T, Rajaraman R, Patel S, Shah R, Srinivasan M, Das M, Ray KJ, Oldenburg CE, McLeod SD, Zegans ME, Acharya NR, Lietman TM, Rose-Nussbaumer J. Predictors of corneal perforation or need for therapeutic keratoplasty in severe fungal keratitis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017;135(9):987. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
