Effects of Electroacupuncture on Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites in Rats with Poststroke Depression
- PMID: 37465562
- PMCID: PMC10350407
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S415098
Effects of Electroacupuncture on Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites in Rats with Poststroke Depression
Abstract
Background: Poststroke depression (PSD) is the most frequent neuropsychiatric consequence of stroke. Electroacupuncture (EA) has been found to be an effective therapy for treating PSD. However, the underlying mechanisms of EA's efficacy remain unclear. This research aimed to investigate the effects of EA on alterations in gut microbiota and fecal metabolome in PSD rats.
Methods: Analyses of gut microbiome and fecal metabolome were performed to identify gut microbes and their functional metabolites in a sham group, PSD group, and EA group. We conducted enrichment analysis to identify the differential metabolic pathways in three groups. Correlations between altered gut microbes and differential metabolites after EA treatment were studied.
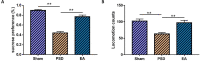
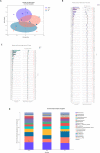
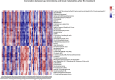
Results: PSD showed decreased species-richness/diversity indices of microbial composition, characterized by an increase in Muribaculaceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, Oscillospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, and Clostridiaceae and a decrease in Lactobacillaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Bacteroidaceae. Of these, the abundance of Muribaculaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, and Clostridiaceae were reversed by EA. Furthermore, PSD was associated with 34 differential fecal metabolites, mainly belonging to steroid hormone biosynthesis, that could be regulated by EA.
Conclusion: Regulation of gut microbiome and lipid metabolism could be one of the potential mechanisms for EA treatment for alleviating the depressive behaviors of PSD.
Keywords: electroacupuncture; fecal metabolome; gut microbiome; metabolic pathways; poststroke depression.
© 2023 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alteration of Gut Microbiome and Correlated Lipid Metabolism in Post-Stroke Depression.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 22;11:663967. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.663967. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33968807 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electroacupuncture on urinary metabolome and microbiota in presenilin1/2 conditional double knockout mice.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 24;13:1047121. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1047121. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36762099 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of gut microbiota and fecal metabolome features among multiple depressive animal models.J Affect Disord. 2022 Oct 1;314:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.088. Epub 2022 Jul 1. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35780963
-
Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids may participate in post-stroke depression by regulating host's lipid metabolism.J Psychiatr Res. 2023 May;161:426-434. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.032. Epub 2023 Apr 4. J Psychiatr Res. 2023. PMID: 37031497
-
Altered Composition of Gut Microbiota in Depression: A Systematic Review.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 10;11:541. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00541. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32587537 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota and functional outcome after ischemic stroke: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 23;15:1414653. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1414653. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39376557 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin Intervention Mitigates Pathological and Behavioral Impairments in APP/PS1 Mice Subjected to Early Social Isolation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70511. doi: 10.1111/cns.70511. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40635450 Free PMC article.
-
Inulin alters gut microbiota to alleviate post-stroke depressive-like behavior associated with the IGF-1-mediated MAPK signaling pathway.Brain Behav. 2024 Jan;14(1):e3387. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3387. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38376033 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant-Like Effects of Electroacupuncture by Regulating NLRP3-mediated Hippocampal Inflammation and Pyroptosis in Rats With Post-Stroke Depression.Brain Behav. 2025 Jul;15(7):e70670. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70670. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40621695 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of arabinoxylan on BDNF/TrkB/p-CREB signaling pathway in the prefrontal cortex and intestinal microbiome in post-stroke depressed rats.BMC Neurosci. 2025 Jul 13;26(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12868-025-00964-6. BMC Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40653476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai W, Mueller C, Li YJ, Shen WD, Stewart R. Post stroke depression and risk of stroke recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;50:102–109. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

