Delayed 18F-FDG PET imaging provides better metabolic asymmetry in potential epileptogenic zone in temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 37465642
- PMCID: PMC10350642
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1180541
Delayed 18F-FDG PET imaging provides better metabolic asymmetry in potential epileptogenic zone in temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the value of 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) two time point imaging for the identification of the potential epileptogenic zone (EZ) in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).
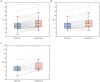
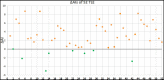
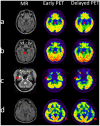
Methods: Fifty-two patients with TLE were prospectively enrolled in the 18F-FDG PET/CT two time point imaging study. The early imaging was obtained approximately 40 min (43.44 ± 18.04 min) after 18F-FDG injection, and the delayed imaging was obtained about 2 to 3 h (160.46 ± 28.70 min) after the injection. Visual and semi-quantitative analysis of 18F-FDG uptake were performed at the two time points in EZ and contralateral symmetrical region. The mean standardized uptake value (SUVmean) of EZ and contralateral symmetrical region was calculated to determine the asymmetry index (AI) of the early and delayed images, as well as in the MRI positive and negative patient groups.
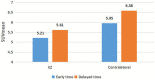
Results: Semi-quantitative analysis demonstrated that AI of the early and delayed 18F-FDG PET/CT images was 13.47 ± 6.10 and 16.43 ± 6.66, respectively. The ΔAI was 2.95 ± 3.05 in 52 TLE patients between the two time points. The AI of the EZ was significantly elevated in delayed images compared to the early images (p < 0.001). The AI of delayed imaging was also significantly elevated compared to the early imaging in both MRI positive (ΔAI = 2.81 ± 2.54, p < 0.001) and MRI negative (ΔAI = 3.21 ± 3.91, p < 0.003) groups, and more pronounced in MRI negative group. Visual analysis also showed that the delayed imaging appeared to be superior to the early imaging for identification of potential EZ.
Conclusion: Delayed 18F-FDG PET imaging provided significantly better than the early imaging in the identification of potential EZ, which can be valuable during epilepsy pre-surgical evaluation in patients with TLE.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET/CT; asymmetry index; potential epileptogenic zone; temporal lobe epilepsy; two time point imaging.
Copyright © 2023 Hong, Fu, Xing, Tao, Zhao, Wang, Chen, You, Ren, Hong, Wang, Zhao, Yang, Zhang, Xu and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of delayed 18F-FDG hybrid PET/MRI for epileptic focus identification: a prospective cohort study.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Jan;48(1):293-301. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04935-3. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32583012
-
18F-flumazenil: a γ-aminobutyric acid A-specific PET radiotracer for the localization of drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy.J Nucl Med. 2013 Aug;54(8):1270-7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.107359. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 23857513 Clinical Trial.
-
[18F]FDG PET/MRI and magnetoencephalography may improve presurgical localization of temporal lobe epilepsy.Eur Radiol. 2022 May;32(5):3024-3034. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08336-4. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34651211
-
Performance of PET imaging for the localization of epileptogenic zone in patients with epilepsy: a meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):6353-6366. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07645-4. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33523306 Review.
-
Applications of global quantitative 18F-FDG-PET analysis in temporal lobe epilepsy.Nucl Med Commun. 2016 Mar;37(3):223-30. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000440. Nucl Med Commun. 2016. PMID: 26588069 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation of Parkinson's disease severity and 18F-FDG and 18F-FP-DTBZ PET.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):3036-3047. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-2047. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235814 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of the 18F-FDG PET and susceptibility-weighted imaging for diagnosis of cerebral glucose metabolism and iron deposition in Parkinson's disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 6;15(1):20029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02672-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40481012 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Radiologists Regarding Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Jul 4;17:3109-3119. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S451301. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38978829 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 18F 9-fluoropropyl-(+)-dihydrotetrabenazine positron emission tomography for distinguishing between early-onset and late-onset idiopathic Parkinson disease and analyzing influencing factors.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Oct 1;14(10):7406-7419. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-804. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39429607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee JJ, Kang WJ, Lee DS, Lee JS, Hwang H, Kim KJ, et al. . Diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET and ictal 99mTc-HMPAO SPET in pediatric temporal lobe epilepsy: quantitative analysis by statistical parametric mapping, statistical probabilistic anatomical map, and subtraction ictal SPET. Seizure. (2005) 14:213–20. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2005.01.010, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

