Third dose of BNT162b2 improves immune response in liver transplant recipients to ancestral strain but not Omicron BA.1 and XBB
- PMID: 37465685
- PMCID: PMC10350672
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206016
Third dose of BNT162b2 improves immune response in liver transplant recipients to ancestral strain but not Omicron BA.1 and XBB
Abstract
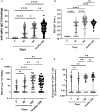
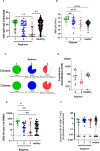
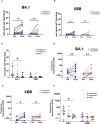
Vaccine immunogenicity in transplant recipients can be impacted by the immunosuppressive (IS) regimens they receive. While BNT162b2 vaccination has been shown to induce an immune response in liver transplant recipients (LTRs), it remains unclear how different IS regimens may affect vaccine immunogenicity after a third BNT162b2 dose in LTRs, which is especially important given the emergence of the Omicron sublineages of SARS-CoV-2. A total of 95 LTRs receiving single and multiple IS regimens were recruited and offered three doses of BNT162b2 during the study period. Blood samples were collected on days 0, 90, and 180 after the first BNT162b2 dose. At each time point, levels of anti-spike antibodies, their neutralizing activity, and specific memory B and T cell responses were assessed. LTRs receiving single IS regimens showed an absence of poor immunogenicity, while LTRs receiving multiple IS regimens showed lower levels of spike-specific antibodies and immunological memory compared to vaccinated healthy controls after two doses of BNT162b2. With a third dose of BNT162b2, spike-specific humoral, memory B, and T cell responses in LTR significantly improved against the ancestral strain of SARS-CoV-2 and were comparable to those seen in healthy controls who received only two doses of BNT162b2. However, LTRs receiving multiple IS regimens still showed poor antibody responses against Omicron sublineages BA.1 and XBB. A third dose of BNT162b2 may be beneficial in boosting antibody, memory B, and T cell responses in LTRs receiving multiple IS regimens, especially against the ancestral Wuhan strain of SARS-CoV-2. However, due to the continued vulnerability of LTRs to presently circulating Omicron variants, antiviral treatments such as medications need to be considered to prevent severe COVID-19 in these individuals.
Keywords: B cells; BNT162b2; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; antibodies; immunosuppressives; liver transplant recipients; spike protein.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Goh, Rouers, Fong, Tay, Chavatte, Hor, Loh, Huang, Tan, Neo, Kam, Yeo, Tan, Huang, Wang, Salleh, Ngoh, Wang, Leo, Lin, Lye, Young, Muthiah, Ng, Rénia and COVID-19 Study Group.
Conflict of interest statement
An application to hold a patent for the SFB assay has been filed (Singapore patent #10202009679P: A Method Of Detecting Antibodies And Related Products). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . . Available at: https://covid19.who.int/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

