Real-time fetal brain tracking for functional fetal MRI
- PMID: 37465882
- PMCID: PMC10952752
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29803
Real-time fetal brain tracking for functional fetal MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To improve motion robustness of functional fetal MRI scans by developing an intrinsic real-time motion correction method. MRI provides an ideal tool to characterize fetal brain development and growth. It is, however, a relatively slow imaging technique and therefore extremely susceptible to subject motion, particularly in functional MRI experiments acquiring multiple Echo-Planar-Imaging-based repetitions, for example, diffusion MRI or blood-oxygen-level-dependency MRI.
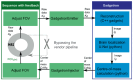
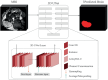
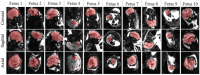
Methods: A 3D UNet was trained on 125 fetal datasets to track the fetal brain position in each repetition of the scan in real time. This tracking, inserted into a Gadgetron pipeline on a clinical scanner, allows updating the position of the field of view in a modified echo-planar imaging sequence. The method was evaluated in real-time in controlled-motion phantom experiments and ten fetal MR studies (17 + 4-34 + 3 gestational weeks) at 3T. The localization network was additionally tested retrospectively on 29 low-field (0.55T) datasets.
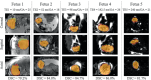
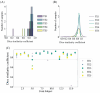
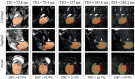
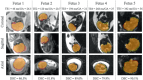
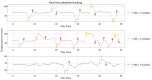
Results: Our method achieved real-time fetal head tracking and prospective correction of the acquisition geometry. Localization performance achieved Dice scores of 84.4% and 82.3%, respectively for both the unseen 1.5T/3T and 0.55T fetal data, with values higher for cephalic fetuses and increasing with gestational age.
Conclusions: Our technique was able to follow the fetal brain even for fetuses under 18 weeks GA in real-time at 3T and was successfully applied "offline" to new cohorts on 0.55T. Next, it will be deployed to other modalities such as fetal diffusion MRI and to cohorts of pregnant participants diagnosed with pregnancy complications, for example, pre-eclampsia and congenital heart disease.
Keywords: BOLD; T2* relaxometry; diffusion MRI; fetal MRI; fetal brain development; motion correction; motion detection; tracking.
© 2023 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Polat A, Barlow S, Ber R, Achiron R, Katorza E. Volumetric MRI study of the intrauterine growth restriction fetal brain. Eur Radiol. 2017;27:2110‐2118. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen AV, Hutter JM, Grant EP, Seed M, Gowland P. T2* weighted placental MRI: basic research tool or an emerging clinical test of placental dysfunction? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019;55:293‐302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

