RNA trafficking and subcellular localization-a review of mechanisms, experimental and predictive methodologies
- PMID: 37466130
- PMCID: PMC10516376
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbad249
RNA trafficking and subcellular localization-a review of mechanisms, experimental and predictive methodologies
Abstract
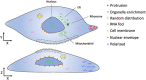
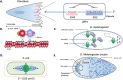
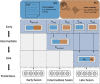
RNA localization is essential for regulating spatial translation, where RNAs are trafficked to their target locations via various biological mechanisms. In this review, we discuss RNA localization in the context of molecular mechanisms, experimental techniques and machine learning-based prediction tools. Three main types of molecular mechanisms that control the localization of RNA to distinct cellular compartments are reviewed, including directed transport, protection from mRNA degradation, as well as diffusion and local entrapment. Advances in experimental methods, both image and sequence based, provide substantial data resources, which allow for the design of powerful machine learning models to predict RNA localizations. We review the publicly available predictive tools to serve as a guide for users and inspire developers to build more effective prediction models. Finally, we provide an overview of multimodal learning, which may provide a new avenue for the prediction of RNA localization.
Keywords: RNA; localization; machine learning; multimodality; subcellular.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Lawrence JB, Singer RH. Intracellular localization of messenger RNAs for cytoskeletal proteins. Cell 1986;45:407–15. - PubMed
-
- Lécuyer E, Yoshida H, Parthasarathy N, et al. Global analysis of mRNA localization reveals a prominent role in organizing cellular architecture and function. Cell 2007;131:174–87. - PubMed
-
- Nevo-Dinur K, Nussbaum-Shochat A, Ben-Yehuda S, Amster-Choder O. Translation-independent localization of mRNA in E. coli. Science 2011;331:1081–4. - PubMed

