Electrostatic Linear Ion Trap Optimization Strategy for High Resolution Charge Detection Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 37466262
- PMCID: PMC10842736
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.3c00177
Electrostatic Linear Ion Trap Optimization Strategy for High Resolution Charge Detection Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
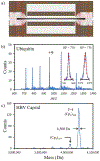
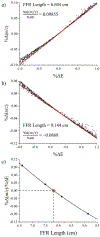
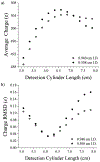
Single ion mass measurements allow mass distributions to be recorded for heterogeneous samples that cannot be analyzed by conventional mass spectrometry. In charge detection mass spectrometry (CD-MS), ions are detected using a conducting cylinder coupled to a charge sensitive amplifier. For optimum performance, the detection cylinder is embedded in an electrostatic linear ion trap (ELIT) where trapped ions oscillate between end-caps that act as opposing ion mirrors. The oscillating ions generate a periodic signal that is analyzed by fast Fourier transforms. The frequency yields the m/z, and the magnitude provides the charge. With a charge precision of 0.2 elementary charges, ions can be assigned to their correct charge states with a low error rate, and the m/z resolving power determines the mass resolving power. Previously, the best mass resolving power achieved with CD-MS was 300. We have recently increased the mass resolving power to 700, through the better optimization of the end-cap potentials. To make a more dramatic improvement in the m/z resolving power, it is necessary to find an ELIT geometry and end-cap potentials that can simultaneously make the ion oscillation frequency independent of both the ion energy and ion trajectory (angular divergence and radial offset) of the entering ion. We describe an optimization strategy that allows these conditions to be met while also adjusting the signal duty cycle to 50% to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio for the charge measurement. The optimized ELIT provides an m/z resolving power of over 300 000 in simulations. Coupled with the high precision charge determination available with CD-MS, this will yield a mass resolving power of 300 000. Such a high mass resolving power will be transformative for the analysis of heterogeneous samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Two of the authors (D.Y.B. and M.F.J.) are shareholders in Megadalton Solutions, a company that is engaged in commercializing CD-MS. D.Y.B. is an employee of Megadalton Solutions, and M.F.J. is a consultant for Waters.
Figures





References
-
- Smith RD; Cheng X; Bruce JE; Hofstadler SA; Anderson GA Trapping, detection and reaction of very large single molecular ions by mass spectrometry. Nature 1994, 369, 137–139.
-
- Bruce JE; Cheng X; Bakhtiar R; Wu Q; Hofstadler SA; Anderson GA; Smith RD Trapping, detection, and mass measurement of individual ions in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1994, 116, 7839–7847.
-
- Chen R; Wu Q; Mitchell DW; Hofstadler SA; Rockwood AL; Smith RD Direct charge number and molecular weight determination of large individual ions by electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 1994, 66, 3964–3969.
-
- Chen R; Cheng X; Mitchell DW; Hofstadler SA; Wu Q; Rockwood AL; Sherman MG; Smith RD Trapping, detection, and mass determination of coliphage T4 DNA ions by electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 1995, 67, 1159–1163.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

