Cardiovascular and health cost impacts of cuff blood pressure underestimation and overestimation of invasive aortic systolic blood pressure
- PMID: 37466429
- PMCID: PMC7614996
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003510
Cardiovascular and health cost impacts of cuff blood pressure underestimation and overestimation of invasive aortic systolic blood pressure
Abstract
Objective: Hypertension management is directed by cuff blood pressure (BP), but this may be inaccurate, potentially influencing cardiovascular disease (CVD) events and health costs. This study aimed to determine the impact on CVD events and related costs of the differences between cuff and invasive SBP.
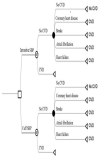
Methods: Microsimulations based on Markov modelling over one year were used to determine the differences in the number of CVD events (myocardial infarction or coronary death, stroke, atrial fibrillation or heart failure) predicted by Framingham risk and total CVD health costs based on cuff SBP compared with invasive (aortic) SBP. Modelling was based on international consortium data from 1678 participants undergoing cardiac catheterization and 30 separate studies. Cuff underestimation and overestimation were defined as cuff SBP less than invasive SBP and cuff SBP greater than invasive SBP, respectively.
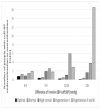
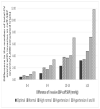
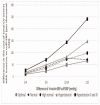
Results: The proportion of people with cuff SBP underestimation versus overestimation progressively increased as SBP increased. This reached a maximum ratio of 16 : 1 in people with hypertension grades II and III. Both the number of CVD events missed (predominantly stroke, coronary death and myocardial infarction) and associated health costs increased stepwise across levels of SBP control, as cuff SBP underestimation increased. The maximum number of CVD events potentially missed (11.8/1000 patients) and highest costs ($241 300 USD/1000 patients) were seen in people with hypertension grades II and III and with at least 15 mmHg of cuff SBP underestimation.
Conclusion: Cuff SBP underestimation can result in potentially preventable CVD events being missed and major increases in health costs. These issues could be remedied with improved cuff SBP accuracy.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bloom DE, Cafiero ET, Jané-Llopis E, Abrahams-Gessel S, Bloom LR, Fathima S, et al. The global economic burden of noncommunicable diseases. Geneva: World Economic Forum; 2011.
-
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 201. Lancet. 2017;390:1345–1422. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Picone DS, Schultz MG, Peng X, Black JA, Dwyer N, Roberts-Thomson P, et al. Discovery of new blood pressure phenotypes and relation to accuracy of cuff devices used in daily clinical practice. Hypertension. 2018;71:1239–1247. - PubMed
-
- Picone DS, Schultz MG, Otahal P, Aakhus S, Al-Jumaily AM, Black JA, et al. Accuracy of cuff-measured blood pressure: systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:572–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

