Comparison of Cardioplegic Solutions in Coronary Bypass Surgery Over Autophagy and Apoptosis Mechanisms
- PMID: 37466618
- PMCID: PMC10364987
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20220479
Comparison of Cardioplegic Solutions in Coronary Bypass Surgery Over Autophagy and Apoptosis Mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) due to myocardial ischemia causes permanent loss of heart tissue.
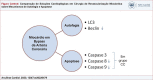
Objectives: We aimed to demonstrate the possible damage to the myocardium at the molecular level through the mechanisms of autophagy and apoptosis in coronary bypass surgery patients.
Methods: One group was administered a Custodiol cardioplegia solution, and the other group was administered a Blood cardioplegia solution. Two myocardial samples were collected from each patient during the operation, just before cardiac arrest and after the aortic cross-clamp was released. The expressions of autophagy and apoptosis markers were evaluated. The level of statistical significance adopted was 5%.
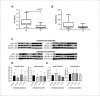
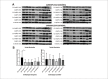
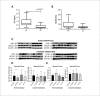
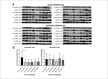
Results: The expression of the BECLIN gene was significant in the myocardial tissues in the BC group (p=0.0078). CASPASE 3, 8, and 9 gene expression levels were significantly lower in the CC group. Postoperative TnT levels were significantly different between the groups (p=0.0072). CASPASE 8 and CASPASE 9 gene expressions were similar before and after aortic cross-clamping (p=0.8552, p=0.8891). In the CC group, CASPASE 3, CASPASE 8, and CASPASE 9 gene expression levels were not found to be significantly different in tissue samples taken after aortic cross-clamping (p=0.7354, p=0.0758, p=0.4128, respectively).
Conclusions: With our findings, we believe that CC and BC solutions do not have a significant difference in terms of myocardial protection during bypass operations.
Fundamento: A doença arterial coronariana (DAC) devido à isquemia miocárdica causa perda permanente de tecido cardíaco.
Objetivos: Nosso objetivo foi demonstrar o possível dano ao miocárdio em nível molecular através dos mecanismos de autofagia e apoptose em pacientes submetidos à cirurgia de revascularização miocárdica.
Métodos: Um grupo recebeu uma solução de cardioplegia Custodiol e o outro grupo uma solução de cardioplegia sanguínea. Duas amostras miocárdicas foram coletadas de cada paciente durante a operação, imediatamente antes da parada cardíaca e após a liberação do pinçamento aórtico. Foram avaliadas as expressões de marcadores de autofagia e apoptose. O nível de significância estatística adotado foi de 5%.
Resultados: A expressão do gene BECLIN foi significativa nos tecidos miocárdicos do grupo CS (p=0,0078). Os níveis de expressão dos genes CASPASE 3, 8 e 9 foram significativamente menores no grupo CC. Os níveis pós-operatórios de TnT foram significativamente diferentes entre os grupos (p=0,0072). As expressões dos genes CASPASE 8 e CASPASE 9 foram semelhantes antes e depois do pinçamento aórtico (p=0,8552, p=0,8891). No grupo CC, os níveis de expressão gênica de CASPASE 3, CASPASE 8 e CASPASE 9 não foram significativamente diferentes em amostras de tecido coletadas após pinçamento aórtico (p=0,7354, p=0,0758, p=0,4128, respectivamente).
Conclusões: Com nossos achados, acreditamos que as soluções CC e CS não apresentam diferença significativa em termos de proteção miocárdica durante as operações de by-pass.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Não há conflito com o presente artigo
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood mRNA Expression Profiles of Autophagy, Apoptosis, and Hypoxia Markers on Blood Cardioplegia and Custodiol Cardioplegia Groups.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021 Jun 1;36(3):331-337. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0330. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33438846 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioplegia Application with A Hand-Squeezed Cardioplegia Bag. Is It Safe?Heart Surg Forum. 2021 Jul 26;24(4):E619-E623. doi: 10.1532/hsf.3933. Heart Surg Forum. 2021. PMID: 34473027
-
Comparison of heat monitoring-based myocardial protection strategy with classic myocardial protection method in isolated coronary artery bypass surgery patients.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2020 Mar-Apr;45:107161. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2019.107161. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31810046
-
The Effects of Amino Acids Enriched Del Nido Cardioplegia on Myocardial Leucocyte Accumulation and Ventricular Functions in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery.Heart Surg Forum. 2021 Jan 15;24(1):E038-E047. doi: 10.1532/hsf.3265. Heart Surg Forum. 2021. PMID: 33635267
-
The effect of leukocyte reduction filters on inflammatory mediator release during coronary artery bypass grafting.Kardiol Pol. 2013;71(9):945-50. doi: 10.5603/KP.2013.0230. Kardiol Pol. 2013. PMID: 24065423 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kocak EF, Kocak C, Aksoy A, Isiklar OO, Akcilar R, Ozdomanic IF, et al. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T is more helpful in detecting peri-operative myocardial injury and apoptosis during coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2015;26(6):234–241. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2015-052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

