Impact of encorafenib on survival of patients with BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer in a real-world setting
- PMID: 37466791
- PMCID: PMC10587317
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05141-y
Impact of encorafenib on survival of patients with BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer in a real-world setting
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have a dismal prognosis. The best strategies in these patients remain elusive. Against this background, we report the clinical course of patients with BRAFV600E-mutant mCRC to retrieve the best treatment strategy.
Patients and methods: Clinico-pathological data were extracted from the electronic health records. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate overall (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Objective response rate (ORR) was assessed according to RECIST 1.1.
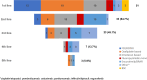
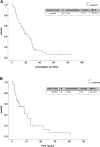
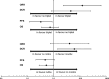
Results: In total, 51 patients were enrolled. FOLFOXIRI was administered to 12 patients; 29 patients received FOLFOX or FOLFIRI as first-line treatment. Median OS was 17.6 months. Median PFS with FOLFOXIRI (13.0 months) was significantly prolonged (HR 0.325) as compared to FOLFOX/FOLFIRI (4.3 months). However, this failed to translate into an OS benefit (p = 0.433). Interestingly, addition of a monoclonal antibody to chemotherapy associated with superior OS (HR 0.523). A total of 64.7% patients received further-line therapy, which included a BRAF inhibitor in 17 patients. Targeted therapy associated with very favourable OS (25.1 months).
Conclusion: Patients with BRAFV600E-mutated mCRC benefit from the addition of an antibody to first-line chemotherapy. Further-line treatment including a BRAF inhibitor has a dramatic impact on survival.
Keywords: BRAFV600E; Chemotherapy; Encorafenib; Metastatic colorectal cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Martin Schuler received honoraria as consultant (compensated) from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BIOCAD, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, Honoraries for CME presentations from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Novartis and Research funding to institution from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers-Squibb Stefan Kasper received honoraria from Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, BMS, Amgen, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier, Incyte, Pierre Fabre and Lilly; research funding from Merck Serono, Lilly, BMS, Roche. Isabel Virchow received travel support from Pierre Fabre. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
MS received honoraria as consultant (compensated) from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BIOCAD, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, Honoraries for CME presentations from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Novartis and Research funding to institution from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers-Squibb. SK received honoraria from Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, BMS, Amgen, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier, Incyte, Pierre Fabre and Lilly; research funding from Merck Serono, Lilly, BMS, Roche. IV received travel support from Pierre Fabre. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Benson AB et al (2021) Colon cancer, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 19(3):329–359 - PubMed
-
- Bray F et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424 - PubMed
-
- Clancy C et al (2013) BRAF mutation is associated with distinct clinicopathological characteristics in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis 15(12):e711-718 - PubMed
-
- Cremolini C et al (2015) FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study. Lancet Oncol 16(13):1306–1315 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

