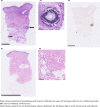
Cutaneous vascular calcifications in patients with chronic kidney disease and calcific uremic arteriolopathy: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37466817
- PMCID: PMC10543801
- DOI: 10.1007/s40620-023-01707-8
Cutaneous vascular calcifications in patients with chronic kidney disease and calcific uremic arteriolopathy: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Calcific uremic arteriolopathy is a life-threatening cutaneous condition in patients with chronic kidney disease. Often, clinical diagnosis is accompanied by histopathologic evaluations demonstrating vascular calcium deposits. We aimed to investigate the presence of cutaneous calcifications in non-lesional tissue in patients with chronic kidney disease, and the relation to systemic vascular calcification.
Methods: We investigated the presence of cutaneous vascular calcifications in non-lesional skin biopsies from patients with current or previous calcific uremic arteriolopathy and patients with different stages of chronic kidney disease without calcific uremic arteriolopathy, and explored their association with vascular calcification in other vascular beds. Systemic vascular calcification was examined by mammography and lumbar X-ray.
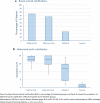
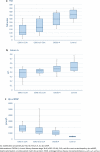
Results: Thirty-nine adults were enrolled (current or previous calcific uremic arteriolopathy, n = 9; end-stage chronic kidney disease, n = 12; chronic kidney disease stage 3b-4, n = 12; healthy controls, n = 6). All calcific uremic arteriolopathy patients had end-stage kidney disease. Cutaneous vascular calcifications were not present in any of the non-lesional skin punch biopsies. Breast arterial calcification was demonstrated in patients with calcific uremic arteriolopathy (75%) and chronic kidney disease (end-stage 67% and stage 3b-4 25%, respectively), but in none of the controls. All chronic kidney disease patients had systemic calcification on lumbar X-ray (median score 21, 22, and 15 in patients with calcific uremic arteriolopathy, end-stage kidney disease and chronic kidney disease stage 3b-4). The serum calcification propensity was significantly different between groups.
Discussion: Despite a high burden of systemic vascular calcification, cutaneous calcium deposits in non-lesional tissue could not be demonstrated histopathologically in patients with chronic kidney disease (with or without current or previous calcific uremic arteriolopathy). Further studies to determine whether these findings are representative or attributed to other factors are warranted.
Keywords: Calcific uremic arteriolopathy; Calcification propensity; Calcifications; Chronic kidney disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A Pasch is an employee and stockholder of Calciscon AG, Biel, Switzerland, which commercializes the T50 test. DH, MD, DK, MR, IV, LL, NJ, LS, DH have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Localization, Morphologic Features, and Chemical Composition of Calciphylaxis-Related Skin Deposits in Patients With Calcific Uremic Arteriolopathy.JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Jul 1;155(7):789-796. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0381. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31116362 Free PMC article.
-
Questionable specificity of histologic findings in calcific uremic arteriolopathy.Kidney Int. 2018 Aug;94(2):390-395. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29885932
-
Calciphylaxis: from the disease to the diseased.J Nephrol. 2015 Oct;28(5):531-40. doi: 10.1007/s40620-015-0192-2. Epub 2015 Apr 3. J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25835730 Review.
-
[Calcific uremic arteriolopathy in hemodialysis patient, review of literature through five cases reports].Nephrol Ther. 2018 Nov;14(6):439-445. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Nephrol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30401462 Review. French.
-
Calcific uremic arteriolopathy (calciphylaxis) calls into question the validity of guidelines of diagnosis and treatment.J Dermatolog Treat. 2020 Aug;31(5):545-548. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1618435. Epub 2019 May 31. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020. PMID: 31075991 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors Associated With the Development of Calciphylaxis in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Dec 8;16(12):e75314. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75314. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39776750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical