A surgically optimized intraoperative poly(I:C)-releasing hydrogel prevents cancer recurrence
- PMID: 37467718
- PMCID: PMC10394259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101113
A surgically optimized intraoperative poly(I:C)-releasing hydrogel prevents cancer recurrence
Abstract
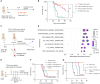
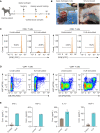
Recurrences frequently occur following surgical removal of primary tumors. In many cancers, adjuvant therapies have limited efficacy. Surgery provides access to the tumor microenvironment, creating an opportunity for local therapy, in particular immunotherapy, which can induce local and systemic anti-cancer effects. Here, we develop a surgically optimized biodegradable hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel for sustained intraoperative delivery of Toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly(I:C) and demonstrate that it significantly reduces tumor recurrence after surgery in multiple mouse models. Mechanistically, poly(I:C) induces a transient interferon alpha (IFNα) response, reshaping the tumor/wound microenvironment by attracting inflammatory monocytes and depleting regulatory T cells. We demonstrate that a pre-existing IFN signature predicts response to the poly(I:C) hydrogel, which sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint therapy. The safety, immunogenicity, and surgical feasibility are confirmed in a veterinary trial in canine soft tissue tumors. The surgically optimized poly(I:C)-loaded hydrogel provides a safe and effective approach to prevent cancer recurrence.
Keywords: PD-1; Toll-like receptor; cancer; drug delivery; hydrogel; immunotherapy; poly(I:C); surgical oncology; tumor; wound healing.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare a patent application pertaining to aspects of this work. B.F.K. discloses a financial interest in OncoRes Medical, a company developing QME for use in surgery. W.J.L. declares consultancy for Douglas Pharmaceuticals and MSD and research funding from Douglas Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and ENA Therapeutics.
Figures





References
-
- Cloughesy T.F., Mochizuki A.Y., Orpilla J.R., Hugo W., Lee A.H., Davidson T.B., Wang A.C., Ellingson B.M., Rytlewski J.A., Sanders C.M., et al. Neoadjuvant anti-pd-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2019;25:477–486. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0337-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

