Monoallelic variation in DHX9, the gene encoding the DExH-box helicase DHX9, underlies neurodevelopment disorders and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- PMID: 37467750
- PMCID: PMC10432148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.06.013
Monoallelic variation in DHX9, the gene encoding the DExH-box helicase DHX9, underlies neurodevelopment disorders and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Abstract
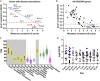
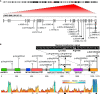
DExD/H-box RNA helicases (DDX/DHX) are encoded by a large paralogous gene family; in a subset of these human helicase genes, pathogenic variation causes neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) traits and cancer. DHX9 encodes a BRCA1-interacting nuclear helicase regulating transcription, R-loops, and homologous recombination and exhibits the highest mutational constraint of all DDX/DHX paralogs but remains unassociated with disease traits in OMIM. Using exome sequencing and family-based rare-variant analyses, we identified 20 individuals with de novo, ultra-rare, heterozygous missense or loss-of-function (LoF) DHX9 variant alleles. Phenotypes ranged from NDDs to the distal symmetric polyneuropathy axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT2). Quantitative Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) analysis demonstrated genotype-phenotype correlations with LoF variants causing mild NDD phenotypes and nuclear localization signal (NLS) missense variants causing severe NDD. We investigated DHX9 variant-associated cellular phenotypes in human cell lines. Whereas wild-type DHX9 was restricted to the nucleus, NLS missense variants abnormally accumulated in the cytoplasm. Fibroblasts from an individual with an NLS variant also showed abnormal cytoplasmic DHX9 accumulation. CMT2-associated missense variants caused aberrant nucleolar DHX9 accumulation, a phenomenon previously associated with cellular stress. Two NDD-associated variants, p.Gly411Glu and p.Arg761Gln, altered DHX9 ATPase activity. The severe NDD-associated variant p.Arg141Gln did not affect DHX9 localization but instead increased R-loop levels and double-stranded DNA breaks. Dhx9-/- mice exhibited hypoactivity in novel environments, tremor, and sensorineural hearing loss. All together, these results establish DHX9 as a critical regulator of mammalian neurodevelopment and neuronal homeostasis.
Keywords: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; DExD/H-box RNA helicases; DHX9; DNA damage repair; R-loops; allelic series; epilepsy; homologous recombination; neurodevelopmental disorders; neuropathy.
Copyright © 2023 American Society of Human Genetics. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.R.L. has stock ownership in 23andMe, is a paid consultant for Genome International, and is a co-inventor on multiple US and European patents related to molecular diagnostics for inherited neuropathies, eye diseases, genomic disorders, and bacterial genomic fingerprinting. The Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at the Baylor College of Medicine receives revenue from clinical genetic testing conducted at Baylor Genetics (BG) Laboratories. F.M. and T.S.-S. are employees of GeneDx.
Figures





References
-
- Snijders Blok L., Madsen E., Juusola J., Gilissen C., Baralle D., Reijnders M.R.F., Venselaar H., Helsmoortel C., Cho M.T., Hoischen A., et al. Mutations in DDX3X are a common cause of unexplained intellectual disability with gender-specific effects on Wnt signaling. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015;97:343–352. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.07.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang X., Posey J.E., Rosenfeld J.A., Bacino C.A., Scaglia F., Immken L., Harris J.M., Hickey S.E., Mosher T.M., Slavotinek A., et al. Phenotypic expansion in DDX3X – a common cause of intellectual disability in females. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018;5:1277–1285. doi: 10.1002/acn3.622. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lennox A.L., Hoye M.L., Jiang R., Johnson-Kerner B.L., Suit L.A., Venkataramanan S., Sheehan C.J., Alsina F.C., Fregeau B., Aldinger K.A., et al. Pathogenic DDX3X mutations impair RNA metabolism and neurogenesis during fetal cortical development. Neuron. 2020;106:404–420.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.01.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007526/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS125126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS105078/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HG008986/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS043124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS134350/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007526/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011758/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

