Screening biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1 overexpression
- PMID: 37468609
- PMCID: PMC10587271
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05160-9
Screening biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1 overexpression
Abstract
Purpose: Immunotherapy plays an important role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); in particular, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy has good therapeutic effects in PD-L1-positive patients. This study aims to screen NSCLC patients with PD-L1-positive expression and select effective biomarkers for ICI immunotherapy.
Methods: Collected tumor samples from the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University and 117 patients with stage III-IV NSCLC were included in the study. All patients were on first- or second-line therapy and not on targeted therapy. Based on the molecular profiles and clinical features, we screened biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1 overexpression.
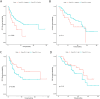
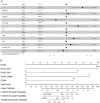
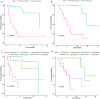
Results: 117 NSCLC patients receiving ICIs immunotherapy were enrolled. First, we found that immunotherapy was more effective in patients with positive PD-L1 expression. Second, we found that ROS1 gene mutations, KRAS gene mutations, tumor stage, and the endocrine system diseases history are independent prognostic factors for PD-L1 positive patients. Then we combined independent risk factors and constructed a new Nomogram to predict the therapeutic efficacy of ICIs immunotherapy in PD-L1 positive patients. The Nomogram integrates these factors into a prediction model, and the predicted C-statistic of 3 months, 6 months and 12 months are 0.85, 0.84 and 0.85, which represents the high predictive accuracy of the model.
Conclusions: We have established a model that can predict the efficacy of ICIs immunotherapy in PD-L1 positive patients. The model consists of ROS1 gene mutations, KRAS gene mutations, tumor staging, and endocrine system disease history, and has good predictive ability.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Immunotherapy; NSCLC; PD-L1.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integration of comprehensive genomic profiling, tumor mutational burden, and PD-L1 expression to identify novel biomarkers of immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Apr;10(7):2216-2231. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3649. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33655698 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Jun;14(6):1095-1101. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Feb 6. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30738221
-
[The efficacy and prognostic factors of immunotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with different driver gene mutations].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 5;102(13):922-929. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20211025-02352. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35385963 Chinese.
-
Immunotherapy Alone or in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020 Jul 27;21(8):69. doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-00768-2. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32720019 Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions.Oncologist. 2019 Feb;24(Suppl 1):S31-S41. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-IO-S1-s05. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30819829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with KRAS mutations: A network meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2024 Apr;18(4):e13745. doi: 10.1111/crj.13745. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 38566277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar E, Ricciuti B, Gainor J, Kehl K, Kravets S, Dahlberg S, Nishino M, Sholl L, Adeni A, Subegdjo S et al (2019) Outcomes to first-line pembrolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and very high PD-L1 expression. Ann Oncol 30(10):1653–1659 - PubMed
-
- Castellanos M, Fanous E, Thaker R, Flory M, Seetharamu N, Dhar M, Starr A, Strange T (2023) Expression patterns and clinical significance of estrogen receptor in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract 241:154298 - PubMed
-
- Chang V, Rhee J, Berndt S, Moore S, Freedman N, Jones R, Silverman D, Gierach G, Hofmann J, Purdue M (2023) Serum perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer according to hormone receptor status: an analysis in the prostate, lung, colorectal and ovarian cancer screening trial. Int J Cancer - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

