Osteomyelitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius in immunocompetent adults - a case report and systematic literature review
- PMID: 37468663
- PMCID: PMC10427518
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-023-04640-7
Osteomyelitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius in immunocompetent adults - a case report and systematic literature review
Abstract
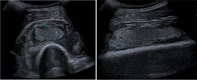
Hematogenous osteomyelitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius is rare, particularly in immunocompetent adults. The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of the clinical presentation, prognosis as well as treatment of this disease, with the focus on immunocompetent adults. Six medical literature libraries were searched to identify studies reporting on Streptococcus intermedius induced hematogenous osteomyelitis in immunocompetent adults. In addition, we presented a case of a 44-year-old man from our institution that is illustrative for this disease. Four case reports describing four patients were identified by this systematic literature review. Hence, the data of five patients (including our case) were assessed. The most common presenting symptom was localised pain, followed by fever. Portal entries were found in two patients (general periodontitis and necrotic dentition). The localisations of osteomyelitis were diverse: femoral (two patients), lumbar spine (two patients), and the iliac bone (one patient). Treatment strategies varied strongly, but antibiotics (penicillins) were administered in each case, and two patients underwent surgical debridement. Follow-up ranged from 2 weeks to more than 6 months; one patient died from septic shock. Only a very limited number of immunocompetent adults with Streptococcus intermedius induced hematogenous osteomyelitis have been described. Based on the available data, we summarised the clinical presentation, prognosis as well as treatment of hematogenous osteomyelitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius in this patient population.
Keywords: Hematogenous; Immunocompetent; Infectious diseases; Osteomyelitis; Streptococcus intermedius.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics for exacerbations of asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 25;6(6):CD002741. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002741.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29938789 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Application of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) in Treatment of Osteomyelitis in Human and Veterinary Orthopedics.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Mar 5;16(3):90. doi: 10.3390/jfb16030090. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40137369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteremia from streptococcus constellatus revealing a gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Gut Pathog. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13099-023-00593-6. Gut Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38178146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whiley RA, Fraser H, Hardie JM, Beighton D. Phenotypic differentiation of Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus strains within the “Streptococcus milleri group”. J Clin Microbiol. 1990;28(7):1497–1501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1497-1501.1990. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

