The application of Aptamer in biomarker discovery
- PMID: 37468977
- PMCID: PMC10354955
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-023-00510-8
The application of Aptamer in biomarker discovery
Abstract
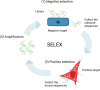
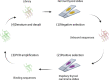
Biomarkers are detectable molecules that can reflect specific physiological states of cells, organs, and organisms and therefore be regarded as indicators for specific diseases. And the discovery of biomarkers plays an essential role in cancer management from the initial diagnosis to the final treatment regime. Practically, reliable clinical biomarkers are still limited, restricted by the suboptimal methods in biomarker discovery. Nucleic acid aptamers nowadays could be used as a powerful tool in the discovery of protein biomarkers. Nucleic acid aptamers are single-strand oligonucleotides that can specifically bind to various targets with high affinity. As artificial ssDNA or RNA, aptamers possess unique advantages compared to conventional antibodies. They can be flexible in design, low immunogenicity, relative chemical/thermos stability, as well as modifying convenience. Several SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) based methods have been generated recently to construct aptamers for discovering new biomarkers in different cell locations. Secretome SELEX-based aptamers selection can facilitate the identification of secreted protein biomarkers. The aptamers developed by cell-SELEX can be used to unveil those biomarkers presented on the cell surface. The aptamers from tissue-SELEX could target intracellular biomarkers. And as a multiplexed protein biomarker detection technology, aptamer-based SOMAScan can analyze thousands of proteins in a single run. In this review, we will introduce the principle and workflow of variations of SELEX-based methods, including secretome SELEX, ADAPT, Cell-SELEX and tissue SELEX. Another powerful proteome analyzing tool, SOMAScan, will also be covered. In the second half of this review, how these methods accelerate biomarker discovery in various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases, will be discussed.
Keywords: Aptamer; Biomarker discovery; Cardiovascular diseases; Neurodegeneration-related diseases; SELEX; SOMAScan; cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cancer protein biomarker discovery based on nucleic acid aptamers.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jul 1;132:190-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.165. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30926499 Review.
-
Advances in Aptamer-Based Biomarker Discovery.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 16;9:659760. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.659760. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33796540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic acid aptamer application in diagnosis and therapy of colorectal cancer based on cell-SELEX technology.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2017 Nov 14;1(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s41698-017-0041-y. eCollection 2017. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29872716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer biomarker discovery using DNA aptamers.Analyst. 2016 Jan 21;141(2):461-6. doi: 10.1039/c5an01918d. Analyst. 2016. PMID: 26567694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SELEX methods on the road to protein targeting with nucleic acid aptamers.Biochimie. 2018 Nov;154:132-155. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 30193856 Review.
Cited by
-
Cornea-SELEX for aptamers targeting the surface of eyes and liposomal drug delivery.Exploration (Beijing). 2024 Feb 9;4(4):20230008. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20230008. eCollection 2024 Aug. Exploration (Beijing). 2024. PMID: 39175889 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer based immunotherapy: a potential solid tumor therapeutic.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1536569. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1536569. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40034705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Functionally Engineered Aptamers: Strategies and Applications.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2025 Aug 18;383(3):30. doi: 10.1007/s41061-025-00516-w. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2025. PMID: 40824336 Review.
-
Surface Functionalization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles with Various Disease-Specific Nonthiolated Aptamers: RSM-Based Optimization for Multifactorial Disease Biomarker Detection.ACS Sens. 2025 Feb 28;10(2):944-953. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c02722. Epub 2025 Feb 17. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 39960422 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamers' Potential to Fill Therapeutic and Diagnostic Gaps.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 12;17(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ph17010105. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aronson JK, Ferner RE. Biomarkers-A General Rev Curr Protoc Pharmacol, 2017. 76: p. 9.23.1–9.23.17. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

