The effects of macro-algae supplementation on serum lipid, glycaemic control and anthropometric indices: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
- PMID: 37469128
- PMCID: PMC10495559
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.439
The effects of macro-algae supplementation on serum lipid, glycaemic control and anthropometric indices: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Abstract
Introduction: Macro-algae products have been shown to ameliorate the metabolic disorders state. Thus, highlighting their function as supplementary therapeutic agents can be a novel strategy for clinical therapies. This systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials aimed to summarize the effect of macro-algae consumption on serum lipid profile, glycaemic control and anthropometric factors.
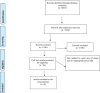
Methods: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, a comprehensive search was performed for relevant studies published up to May 2023. The Cochran's Q test and I-square (I2 ) tests were used to evaluate heterogeneity across the included studies. The meta-analysis was conducted using random-effects model (DerSimonian and Laird), and weighted mean difference (WMD) was considered as the pooled effect size.
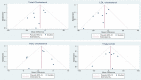
Results: Out of 8602 papers in the initial screening, eight clinical trials with a total of 438 participants were included into this meta-analysis. The results indicated that macro-algae supplementation significantly decreased serum levels of total cholesterol (TC) (WMD = -6.7 mg/dL; 95% CI: -12.59, -0.80; item = 0.026) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) (WMD = -8.25 mg/dL; 95% CI: -15.38, -1.12; p-value = .023). There was an increase in level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) (WMD = 0.48 mg/dL; 95% CI: -2.05, 3.01; p-value = .71) which was not statistically significant. Macro-algae supplementation reduced body mass index (BMI) (WMD = -0.28 kg/m2 ; 95% CI: -0.96, 0.41; p-value = .426), weight (WMD = -0.39 kg; 95% CI: -3.6, 2.83; p-value = .81), waist circumference (WC) (WMD = -0.52 cm; 95% CI: -2.71, 1.66; p-value = .64), fasting blood sugar (FBS) (WMD = -1.95 mg/dL; 95% CI: -5.19, 1.28; p-value = .24) and HbA1c (WMD = -0.02%; 95% CI: -0.14, 0.09; p-value = .66) in intervention group.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis indicated that macro-algae supplementation significantly decreased TC and LDL-c level. It can also increase HDL-c level and reduce anthropometric indices and glycaemic control factors.
Keywords: glycaemic control; integrative medicine; lipid profile; macro-algae; meta-analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors read the manuscript before the submission process, and they declared that there was no conflict of interest to list their name in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Rasouli H, Hosseini‐Ghazvini SM‐B, Khodarahmi R. Therapeutic potentials of the most studied flavonoids: highlighting antibacterial and antidiabetic functionalities. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. 2019;60:85‐122.
-
- Popovic‐Djordjevic JB, Jevtic II, Stanojkovic TP. Antidiabetics: structural diversity of molecules with a common aim. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(18):2140‐2165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

