Alcohol reshapes a liver premetastatic niche for cancer by extra- and intrahepatic crosstalk-mediated immune evasion
- PMID: 37469143
- PMCID: PMC10492032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.07.012
Alcohol reshapes a liver premetastatic niche for cancer by extra- and intrahepatic crosstalk-mediated immune evasion
Abstract
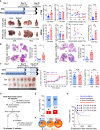
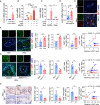
Cancer metastatic organotropism is still a mystery. The liver is known to be susceptible to cancer metastasis and alcoholic injury. However, it is unclear whether and how alcohol facilitates liver metastasis and how to intervene. Here, we show that alcohol preferentially promotes liver metastasis in colon-cancer-bearing mice and post-surgery pancreatic cancer patients. The mechanism is that alcohol triggers an extra- and intrahepatic crosstalk to reshape an immunosuppressive liver microenvironment. In detail, alcohol upregulates extrahepatic IL-6 and hepatocellular IL-6 receptor expression, resulting in hepatocyte STAT3 signaling activation and downstream lipocalin-2 (Lcn2) upregulation. Furthermore, LCN2 promotes T cell-exhaustion neutrophil recruitment and cancer cell epithelial plasticity. In contrast, knocking out hepatocellular Stat3 or systemic Il6 in alcohol-treated mice preserves the liver microenvironment and suppresses liver metastasis. This mechanism is reflected in hepatocellular carcinoma patients, in that alcohol-associated signaling elevation in noncancerous liver tissue indicates adverse prognosis. Accordingly, we discover a novel application for BBI608, a small molecular STAT3 inhibitor that can prevent liver metastasis. BBI608 pretreatment protects the liver and suppresses alcohol-triggered premetastatic niche formation. In conclusion, under extra- and intrahepatic crosstalk, the alcoholic injured liver forms a favorable niche for cancer cell metastasis, while BBI608 is a promising anti-metastatic agent targeting such microenvironments.
Keywords: BBI608; STAT3; alcohol; lipocalin-2; liver; premetastatic niche; tumor targeting strategy.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Similar articles
-
IL6/STAT3 Signaling Orchestrates Premetastatic Niche Formation and Immunosuppressive Traits in Lung.Cancer Res. 2020 Feb 15;80(4):784-797. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2013. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31848193
-
CXCL1 Is Critical for Premetastatic Niche Formation and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 1;77(13):3655-3665. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3199. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28455419 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Premalignant Lesions Secrete Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-1, Which Activates Hepatic Stellate Cells Via CD63 Signaling to Create a Premetastatic Niche in the Liver.Gastroenterology. 2016 Nov;151(5):1011-1024.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.043. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27506299
-
Roles of exosomes in liver metastases: Novel diagnosis and treatment choices.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Dec;234(12):21588-21600. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28785. Epub 2019 May 15. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31093975 Review.
-
Premetastatic niche formation in the liver: emerging mechanisms and mouse models.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Nov;93(11):1193-201. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1342-7. Epub 2015 Sep 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26400831 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver Metastasis in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Management.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 27;6(3):e70119. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70119. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40027151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex role of neutrophils in the tumor microenvironment: an avenue for novel immunotherapies.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 Sep 19;21(10):849-63. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0192. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39297568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic prospect of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in liver cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04983-5. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38519710 Review.
-
NUSAP1 Promotes Immunity and Apoptosis by the SHCBP1/JAK2/STAT3 Phosphorylation Pathway to Induce Dendritic Cell Generation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Immunother. 2025 Feb-Mar 01;48(2):46-57. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000531. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Immunother. 2025. PMID: 38980111 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Infiltration of T-Cell Populations in Tumor and Liver Tissues Predicts Recurrence-Free Survival in Surgically Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 2;17(9):1548. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091548. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361474 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

