Exopolysaccharide is the potential effector of Lactobacillus fermentum PS150, a hypnotic psychobiotic strain
- PMID: 37469436
- PMCID: PMC10352126
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1209067
Exopolysaccharide is the potential effector of Lactobacillus fermentum PS150, a hypnotic psychobiotic strain
Abstract
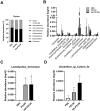
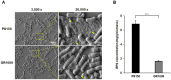
Psychobiotics are a class of probiotics that confer beneficial effects on the mental health of the host. We have previously reported hypnotic effects of a psychobiotic strain, Lactobacillus fermentum PS150 (PS150), which significantly shortens sleep latency in experimental mice, and effectively ameliorate sleep disturbances caused by either caffeine consumption or a novel environment. In the present study, we discovered a L. fermentum strain, GR1009, isolated from the same source of PS150, and found that GR1009 is phenotypically distinct but genetically similar to PS150. Compared with PS150, GR1009 have no significant hypnotic effects in the pentobarbital-induced sleep test in mice. In addition, we found that heat-killed PS150 exhibited hypnotic effects and altered the gut microbiota in a manner similar to live bacteria, suggesting that a heat-stable effector, such as exopolysaccharide (EPS), could be responsible for these effects. Our comparative genomics analysis also revealed distinct genetic characteristics in EPS biosynthesis between GR1009 and PS150. Furthermore, scanning electron microscopy imaging showed a sheet-like EPS structure in PS150, while GR1009 displayed no apparent EPS structure. Using the phenol-sulfate assay, we found that the sugar content value of the crude extract containing EPS (C-EPS) from PS150 was approximately five times higher than that of GR1009, indicating that GR1009 has a lower EPS production activity than PS150. Through the pentobarbital-induced sleep test, we confirmed the hypnotic effects of the C-EPS isolated from PS150, as evidenced by a significant reduction in sleep latency and recovery time following oral administration in mice. In summary, we utilized a comparative approach to delineate differences between PS150 and GR1009 and proposed that EPS may serve as a key factor that mediates the observed hypnotic effect.
Keywords: EPS; Lactobacillus fermentum; PS150; exopolysaccharide; heat-killed; hypnotic; postbiotic.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Chu, Wu, Deng, Wen, Chien, Chao, Chen, Lu and Tsai.
Conflict of interest statement
C-LH, P-JW, F-SD, and C-CW are employed by Bened Biomedical Co., Ltd. Y-CT is a stockholder and a consultant of Bened Biomedical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hypnotic Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum PS150TM on Pentobarbital-Induced Sleep in Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 9;11(10):2409. doi: 10.3390/nu11102409. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31600934 Free PMC article.
-
Safety evaluation of Limosilactobacillus fermentum PS150 for use as a commercial psychobiotic.Food Chem Toxicol. 2025 Mar;197:115312. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2025.115312. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Food Chem Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39922479
-
Lactobacillus fermentum PS150 promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep in the first night effect of mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 11;11(1):16313. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95659-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381098 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus fermentum: Could EPS production ability be responsible for functional properties?Food Microbiol. 2020 Sep;90:103465. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103465. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32336376 Review.
-
Interactions of Surface Exopolysaccharides From Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Within the Intestinal Environment.Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 11;9:2426. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02426. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30364185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanovesicular Mediation of the Gut-Brain Axis by Probiotics: Insights into Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Biology (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;13(5):296. doi: 10.3390/biology13050296. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785778 Free PMC article.
-
Commensal bacterial glycosylation at the interface of host-bacteria interactions.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2545421. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2545421. Epub 2025 Aug 14. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 40810484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Postbiotics Represent a New Strategy for NEC?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1449:43-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58572-2_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39060730 Review.
References
-
- Ale E. C., Batistela V. A., Olivar G. C., Ferrado J. B., Sadiq S., Ahmed H. I., et al. (2020a). Statistical optimisation of the exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus fermentum Lf2 and analysis of its chemical composition. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 73, 76–87. doi: 10.1111/1471-0307.12639 - DOI
-
- Ale E. C., Perezlindo M. J., Pavon Y., Peralta G. H., Costa S., Sabbag N., et al. (2016). Technological, rheological and sensory characterizations of a yogurt containing an exopolysaccharide extract from Lactobacillus fermentum Lf2, a new food additive. Food Res. Int. 90, 259–267. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.10.045, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aryantini N. P., Prajapati J. B., Urashima T., Fukuda K. (2017). Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC 25067 (formerly TDS030603), a viscous exopolysaccharide-producing strain isolated from Indian fermented Milk. Genome Announc. 5:e00091-17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00091-17, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown A. J., Goldsworthy S. M., Barnes A. A., Eilert M. M., Tcheang L., Daniels D., et al. (2003). The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11312–11319. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211609200, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

