Exposure to Dichlorvos pesticide alters the morphology of and lipid metabolism in the ventral prostate of rats
- PMID: 37469457
- PMCID: PMC10352615
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2023.1207612
Exposure to Dichlorvos pesticide alters the morphology of and lipid metabolism in the ventral prostate of rats
Abstract
Organophosphate pesticides are widely used in agriculture, leading to soil, water, and food contamination. Among these compounds is Dichlorvos [O,O-dimethyl O-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)phosphate, DDVP], which is listed as a highly toxic compound by the Environmental Protection Agency and World Health Organization. Exposure to DDVP can result in nervous, respiratory, hepatic, and reproductive abnormalities, in addition to endocrine disrupting, mutagenic, and carcinogenic effects. Little is known about the impacts of DDVP on the reprogramming of lipid metabolism, which is also associated with the development and progression of cancer, since the tumor cells need to recruit, capture, and use fatty acids to compose their building membranes. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of the pesticide DDVP on lipid metabolism in the prostate, after chemical induction by the carcinogen N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU). For this, 32 Fischer rats aged 90 days were randomly divided into four experimental groups: Control, DDVP, MNU, and MNU + DDVP. The MNU and MNU + DDVP groups underwent chemical induction with MNU (15 mg/kg) and the DDVP and MNU + DDVP groups received a diet supplemented with DDVP (10 mg/kg). Histopathological analyses of the rat ventral prostate showed 100% incidence of epithelial hyperplasia in the MNU and MNU + DDVP groups. This finding was accompanied by an increase of the epithelial compartment in the MNU + DDVP group. Immunolocalization of important proteins linked to lipid metabolism has been established. In the MNU + DDVP group, Western blotting analyses pointed out an increased expression of the protein LIMP II (Lysosomal Integral Membrane Protein-II), which is correlated with the capture and distribution of lipids in tumor cells. Together, these results indicate that the association of a low dose of DDVP with MNU was able to promote alterations in the morphology and lipid metabolism of the rat ventral prostate, which may be related to tumor progression in this organ.
Keywords: CD36; Dichlorvos; LIMP-II; SCAP; SREBP; lipid metabolism; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Quintino-Ottonicar, Silva, Maria, Pizzo, Santana, Lenharo, Pinho and Pereira.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
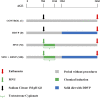
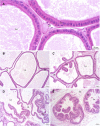


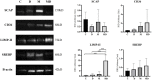
References
-
- Bosland M. C., Prinsen M. K., Dirksen T. J., Spit B. J. (1990). Characterization of adenocarcinomas of the dorsolateral prostate induced in Wistar rats by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea, 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene, and 3,2'-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl, following sequential treatment with cyproterone acetate and testosterone propionate. Cancer Res. 50, 700–709. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

