A rat model of metabolic syndrome-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction phenotype: pathological alterations and possible molecular mechanisms
- PMID: 37469482
- PMCID: PMC10352810
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1208370
A rat model of metabolic syndrome-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction phenotype: pathological alterations and possible molecular mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) represents a syndrome involving multiple pathophysiologic disorders and clinical phenotypes. This complexity makes it challenging to develop a comprehensive preclinical model, which presents an obstacle to elucidating disease mechanisms and developing new drugs. Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a major phenotype of HFpEF. Thus, we produced a rat model of the MetS-related HFpEF phenotype and explored the molecular mechanisms underpinning the observed pathological changes.
Methods: A rat model of the MetS-related HFpEF phenotype was created by feeding spontaneously hypertensive rats a high-fat-salt-sugar diet and administering streptozotocin solution intraperitoneally. Subsequently, pathological changes in the rat heart and their possible molecular mechanisms were explored.
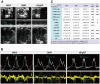
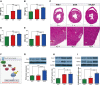
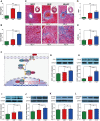
Results: The HFpEF rats demonstrated primary features of MetS, such as hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, and cardiac anomalies, such as left ventricular (LV) remodeling and diastolic impairment, and left atrial dilation. Additionally, inflammation, myocardial hypertrophy, and fibrosis were observed in LV myocardial tissue, which may be associated with diverse cellular and molecular signaling cascades. First, the inflammatory response might be related to the overexpression of inflammatory regulators (growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and vascular endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)). Secondly, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) may stimulate cardiac hypertrophy, which was regulated by activated -RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT). Finally, the transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)/Smads pathway might regulate collagen production and fibroblast activation, promoting myocardial fibrosis.
Conclusion: The HFpEF rat replicates the pathology and clinical presentation of human HFpEF with MetS and may be a reliable preclinical model that helps elucidate HFpEF pathogenesis and develop effective treatment strategies.
Keywords: AKT/GSK-3β; GDF-15; ICAM-1; TGF-β1/Smad; VCAM-1; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; metabolic syndrome.
© 2023 Shi, Liu, Yang, Qiao, Liu, Liu and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

