THE USE OF ADHESIVE RADIOPAQUE GRIDS IN GENICULAR NERVE BLOCK BY RADIOSCOPY
- PMID: 37469498
- PMCID: PMC10353872
- DOI: 10.1590/1413-785220233103e266060
THE USE OF ADHESIVE RADIOPAQUE GRIDS IN GENICULAR NERVE BLOCK BY RADIOSCOPY
Abstract
The performance of genicular nerve block requires an imaging method to guide the procedure. Radioscopy has the disadvantage of being radiation dependent.
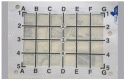
Objective: To assess whether the use of adhesive radiopaque grids reduce radiation exposure in these cases.
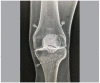
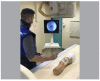
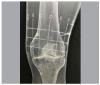
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study conducted with 23 orthopedists in which needles were positioned in a model with and without the use of adhesive radiopaque grids. The number of fluoroscopy shots necessary for proper positioning in three points (superior lateral, superior medial, and inferior medial) were registered.
Results: A statistical difference was observed in the three blocking points studied. The number of radioscopies required for these three points were 12.1 ± 2.5 in the group without grid and 5.0 ± 1.8 in the group with grid. The superior medial point presented the greatest numerical difference and the inferior medial point the smallest.
Conclusion: The use of adhesive radiopaque grids led to a statistically significant reduction in the number of radioscopies/fluoroscopies required to perform the genicular block. The use of this device increases the safety of the physician and patient by reducing radiation exposure in this procedure. Level of Evidence III, Level of Evidence II, Random Clinical Trial.
Para a realização do bloqueio de nervos geniculares é necessário guiar o procedimento por um método de imagem. A radioscopia possui a desvantagem de ser dependente de radiação.
Objetivo: Avaliar se o uso de máscaras localizadoras diminui a exposição à radiação nesses casos.
Métodos: Estudo transversal realizado com 23 ortopedistas, que realizaram o posicionamento de agulhas em um modelo com e sem o uso da máscara localizadora. Foi registrado o número de escopias necessárias para o posicionamento adequado em três pontos: superior lateral, superior medial e inferior medial.
Resultados: Foi observada diferença estatística nos três pontos de bloqueio analisados. O número de radioscopias necessárias nos três pontos somados foi de 12,1 ± 2,5, no grupo sem máscara, e 5,0 ± 1,8, no grupo com máscara. O ponto superior medial foi o que apresentou a maior diferença numérica, e o inferior medial a menor.
Conclusão: O uso da máscara localizadora reduziu de forma estatisticamente significativa o número de escopias necessárias para a realização do bloqueio genicular. O uso desse dispositivo aumenta a segurança do médico e do paciente por diminuir a exposição à radioscopia nesse procediment. Nível de Evidência III, Ensaio clínico randomizado aberto - Nível de recomendação B - nível de evidência 2b.
Keywords: Nerve Block; Orthopedic Surgeons; Peripheral Nerves.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest related to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Prospective Randomized Comparison of the Efficacy of Ultrasound- vs Fluoroscopy-Guided Genicular Nerve Block for Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis.Pain Physician. 2019 Mar;22(2):139-146. Pain Physician. 2019. PMID: 30921977 Clinical Trial.
-
Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Genicular Nerve Block: A Cadaveric Study.Pain Physician. 2015 Sep-Oct;18(5):E899-904. Pain Physician. 2015. PMID: 26431143
-
Ultrasound-guided Genicular Nerve Blockade With Pharmacological Agents for Chronic Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Pain Physician. 2022 Jul;25(4):E489-E502. Pain Physician. 2022. PMID: 35793174
-
Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation for Painful Knee Arthritis: The Why and the How.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2019 Mar 13;9(1):e10. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.18.00016. eCollection 2019 Mar 26. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2019. PMID: 31333900 Free PMC article.
-
Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Painful Knee Osteoarthritis: Current Evidence and Future Directions.Pain Med. 2021 Jul 25;22(Suppl 1):S20-S23. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnab129. Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 34308957 Review.
References
-
- Qudsi-Sinclair S, Borrás-Rubio E, Abellan-Guillén JF, Padilla Del Rey ML, Ruiz-Merino G. A comparison of genicular nerve treatment using either radiofrequency or analgesic block with corticosteroid for pain after a total knee arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized clinical study. Pain Pract. 2017;17(5):578–588. - PubMed
-
- Choi WJ, Hwang SJ, Song JG, Leem JG, Kang YU, Park PH, Shin JW. Radiofrequency treatment relieves chronic knee osteoarthritis pain: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Pain. 2011;152(3):481–487. - PubMed
-
- Sari S, Aydin ON, Turan Y, Sen S, Özlülerden P, Ömürlü I, Gulasti F. Which imaging method should be used for genicular nerve radio frequency thermocoagulation in chronic knee osteoarthritis? J Clin Monit Comput. 2017;31(4):797–803. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz V, Umay E, Gundogdu I, Aras B. The comparison of efficacy of single intraarticular steroid injection versus the combination of genicular nerve block and intraarticular steroid injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomised study. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021;105(1):89–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
