Dissipation Mechanisms and Superlubricity in Solid Lubrication by Wet-Transferred Solution-Processed Graphene Flakes: Implications for Micro Electromechanical Devices
- PMID: 37469503
- PMCID: PMC10352959
- DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.3c01477
Dissipation Mechanisms and Superlubricity in Solid Lubrication by Wet-Transferred Solution-Processed Graphene Flakes: Implications for Micro Electromechanical Devices
Abstract
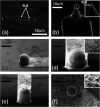
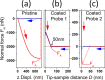
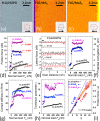
Solution-processed few-layer graphene flakes, dispensed to rotating and sliding contacts via liquid dispersions, are gaining increasing attention as friction modifiers to achieve low friction and wear at technologically relevant interfaces. Vanishing friction states, i.e., superlubricity, have been documented for nearly-ideal nanoscale contacts lubricated by individual graphene flakes. However, there is no clear understanding if superlubricity might persist for larger and morphologically disordered contacts, as those typically obtained by incorporating wet-transferred solution-processed flakes into realistic microscale contact junctions. In this study, we address the friction performance of solution-processed graphene flakes by means of colloidal probe atomic force microscopy. We use a state-of-the-art additive-free aqueous dispersion to coat micrometric silica beads, which are then sled under ambient conditions against prototypical material substrates, namely, graphite and the transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) MoS2 and WS2. High resolution microscopy proves that the random assembly of the wet-transferred flakes over the silica probes results into an inhomogeneous coating, formed by graphene patches that control contact mechanics through tens-of-nanometers tall protrusions. Atomic-scale friction force spectroscopy reveals that dissipation proceeds via stick-slip instabilities. Load-controlled transitions from dissipative stick-slip to superlubric continuous sliding may occur for the graphene-graphite homojunctions, whereas single- and multiple-slips dissipative dynamics characterizes the graphene-TMD heterojunctions. Systematic numerical simulations demonstrate that the thermally activated single-asperity Prandtl-Tomlinson model comprehensively describes friction experiments involving different graphene-coated colloidal probes, material substrates, and sliding regimes. Our work establishes experimental procedures and key concepts that enable mesoscale superlubricity by wet-transferred liquid-processed graphene flakes. Together with the rise of scalable material printing techniques, our findings support the use of such nanomaterials to approach superlubricity in micro electromechanical systems.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang Y.; Zhang D.; Wang Y.; Liu Q.; Li Q.; Dong M. Atomic-Scale Friction of Black and Violet Phosphorus Crystals: Implications for Phosphorus-Based Devices and Lubricants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 9932–9937. 10.1021/acsanm.1c02593. - DOI
-
- Marian M.; Berman D.; Rota A.; Jackson R. L.; Rosenkranz A. Layered 2D Nanomaterials to Tailor Friction and Wear in Machine Elements—A Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101622.10.1002/admi.202101622. - DOI
-
- Morstein C. E.; Dienwiebel M. Graphite Lubrication Mechanisms Under High Mechanical Load. Wear 2021, 203794.10.1016/j.wear.2021.203794. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
