Brodalumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in a real-life setting: a 3 years multicenter retrospective study-IL PSO (Italian landscape psoriasis)
- PMID: 37469659
- PMCID: PMC10352451
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1196966
Brodalumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in a real-life setting: a 3 years multicenter retrospective study-IL PSO (Italian landscape psoriasis)
Abstract
Introduction: Brodalumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the subunit A of the interleukin-17A receptor (IL17RA), inhibiting the signaling of various isoforms of the IL-17 family. It has been approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis after being evaluated in three Phase-3 trials. However, long-term data on brodalumab in a real-life setting are still limited.
Methods: The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term effectiveness and safety of brodalumab in psoriasis. We also assessed the drug survival of brodalumab in a 3 years timespan. We conducted a retrospective multicenter study on 606 patients followed up at 14 Italian dermatology units, all treated with brodalumab according to Italian guidelines. Patients' demographics and disease characteristics were retrieved from electronic databases. At baseline and weeks 12, 24, 52, 104 and 156, we evaluated the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score and investigated for adverse events. The proportions of patients reaching 75, 90 and 100% (PASI 75, PASI 90 and PASI 100, respectively) improvement in PASI, compared with baseline, were also recorded.
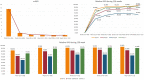
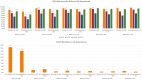
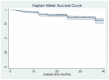
Results: At week 12, 63.53% of the patients reached PASI 90 and 49.17% PASI 100. After 3 years of treatment, 65.22% of patients maintained a complete skin clearance, and 91.30% had an absolute PASI of 2 or less. Patients naïve to biological therapies had better clinical responses at weeks 12, 24 and 52. However, after 2 years of treatment, no significant differences were observed. Body mass index did not interfere with the effectiveness of brodalumab throughout the study. No new safety findings were recorded. After 36 months, 85.64% of our patients were still on treatment with brodalumab.
Conclusion: Our data confirm the effectiveness and the safety of brodalumab in the largest real-life cohort to date, up to 156 weeks.
Keywords: brodalumab; psoriasis; psoriasis treatment; psoriatic arthritis; real-life.
Copyright © 2023 Gargiulo, Ibba, Malagoli, Amoruso, Argenziano, Balato, Bardazzi, Burlando, Carrera, Damiani, Dapavo, Dini, Fabbrocini, Franchi, Gaiani, Girolomoni, Guarneri, Lasagni, Loconsole, Marzano, Megna, Sampogna, Travaglini, Costanzo and Narcisi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Narcisi A, Valenti M, Gargiulo L, Ibba L, Amoruso F, Argenziano G, et al. Real-life effectiveness of tildrakizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis: a 52 weeks multicentre retrospective study-IL PSO (Italian landscape psoriasis). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2023) 37:93–103. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18594, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gargiulo L, Ibba L, Malagoli P, Angileri RG, Bardazzi F, Bernardini N, et al. Real-life effectiveness and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: a 104 weeks multicenter retrospective study—IL PSO (Italian landscape psoriasis). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2023) 37:1017–27. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18913, PMID: - DOI - PubMed

