The role of single protein elasticity in mechanobiology
- PMID: 37469679
- PMCID: PMC7614781
- DOI: 10.1038/s41578-022-00488-z
The role of single protein elasticity in mechanobiology
Abstract
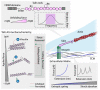
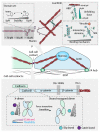
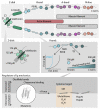
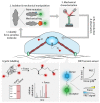
In addition to biochemical signals and genetic considerations, mechanical forces are rapidly emerging as a master regulator of human physiology. Yet the molecular mechanisms that regulate force-induced functionalities across a wide range of scales, encompassing the cell, tissue or organ levels, are comparatively not so well understood. With the advent, development and refining of single molecule nanomechanical techniques, enabling to exquisitely probe the conformational dynamics of individual proteins under the effect of a calibrated force, we have begun to acquire a comprehensive knowledge on the rich plethora of physicochemical principles that regulate the elasticity of single proteins. Here we review the major advances underpinning our current understanding of how the elasticity of single proteins regulates mechanosensing and mechanotransduction. We discuss the present limitations and future challenges of such a prolific and burgeoning field.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
