Deep sedation protocol during atrial fibrillation ablation using a novel variable-loop biphasic pulsed field ablation catheter
- PMID: 37470452
- PMCID: PMC10434733
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euad222
Deep sedation protocol during atrial fibrillation ablation using a novel variable-loop biphasic pulsed field ablation catheter
Abstract
Background: Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is a novel, largely nonthermal ablative modality that, by virtue of its putative preferential action on myocardial tissue through the process of irreversible electroporation (IRE), may replace conventional thermal ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF). The recent inspIRE study confirmed safety and effectiveness of a fully integrated biphasic PFA system with a variable loop circular catheter for the treatment of paroxysmal AF. The majority of PFA procedures were performed using general anesthesia. However, due to the risks of general anesthesia we report the data regarding our sedation protocol used during inspIRE study.
Methods: A total of 29 patients (mean age 55±9 years; 72% male) were enrolled as part of this analysis within the inspIRE trial. The sedation protocol is reported in the manuscript. The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS), the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and the Patient State Index were collected during sedation. Each patient was monitored using the Masimo Sedline. At the end of ablation, the Likert Scale Questionnaire (LSQ) was used to assess the patients' satisfaction with intraoperative analgesia-sedation.
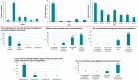
Results: No procedural complications were documented. Sufficient oxygen saturation was maintained in all patients during procedure. Non-invasive ventilation or tracheal intubation were not required for any patient. The RAAS score between -1 to -5 was obtained in 27 patients (93%) while the value 0 was obtained in 2 patients (7%). The VAS score between 0 to 2 was obtained in 24 patients (83%); the VAS score 3 in 3 patients (10%) and the VAS score 4 in 2 patients (7%). The PSI score <50 was achieved in 16 patients (55%) while the PSI between 50 and 70 was achieved in 9 patients (31%). Positive answers to LSQ were obtained in most patients.
Conclusion: During PFA ablation procedures with the variable-loop circular catheter and its accompanying biphasic pulse, our deep sedation protocol is a valid alternative to general anesthesia.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Catheter ablation; Electroporation; Pulmonary vein isolation; Pulsed field ablation; Sedation protocol.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M.G. holds an agreement with Biosense Webster on new technologies development. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Deep sedation for pulsed field ablation by electrophysiology staff: can and should we do it?Europace. 2023 Aug 2;25(9):euad234. doi: 10.1093/europace/euad234. Europace. 2023. PMID: 37515587 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Garcia R, Waldmann V, Vanduynhoven P, Nesti M, Jansen de Oliveira Figueiredo M, Narayanan Ket al. . Worldwide sedation strategies for atrial fibrillation ablation: current status and evolution over the last decade. Europace 2021;23:2039–45. - PubMed
-
- Servatius H, Küffer T, Baldinger SH, Asatryan B, Seiler J, Tanner Het al. . Dexmedetomidine versus propofol for operator-directed nurse-administered procedural sedation during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled study. Heart Rhythm 2022;19:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Grimaldi M, Di Monaco A, Gomez T, Berman D, Datta K, Sharma Tet al. . Time course of irreversible electroporation lesion development through short- and long-term follow-up in pulsed-field ablation-treated hearts. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2022;15:e010661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical