Longitudinal assessment of spiral and uterine arteries in normal pregnancy using novel ultrasound tool
- PMID: 37470712
- PMCID: PMC10801897
- DOI: 10.1002/uog.26312
Longitudinal assessment of spiral and uterine arteries in normal pregnancy using novel ultrasound tool
Abstract
Objectives: To use superb microvascular imaging (SMI) to evaluate longitudinally spiral artery (SA) and uterine artery (UtA) vascular adaptation in normal human pregnancy, and to develop reference ranges for use at various gestational ages throughout pregnancy.
Methods: The data for this study were obtained from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Human Placenta Project. Women aged 18-35 years, with a body mass index < 30 kg/m2 , without comorbidities, with a singleton gestation conceived spontaneously, and gestational age at or less than 13 + 6 weeks were eligible for inclusion. The current analysis was restricted to uncomplicated pregnancies carried to term. Exclusion criteria included maternal or neonatal complications, fetal or umbilical cord anomalies, abnormal placental implantation or delivery < 37 weeks. Women who fulfilled the inclusion criteria formed the reference population of the Human Placenta Project study. Each participant underwent eight ultrasound examinations during pregnancy. The pulsatility index (PI) of both the left and right UtA were obtained twice for each artery and the presence or absence of a notch was noted. Using SMI technology, the total number of SA imaged was recorded in a sagittal placental section at the level of cord insertion. The PI and peak systolic velocity (PSV) were also measured in a total of six SA, including two in the central portion of the placenta, two peripherally towards the uterine fundal portion, and two peripherally towards the lower uterine segment.
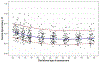
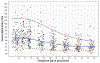
Results: A total of 90 women fulfilled the study criteria. Maternal UtA-PI decreased throughout the first half of pregnancy from a mean ± SD of 1.39 ± 0.50 at 12-13 weeks' gestation to 0.88 ± 0.24 at 20-21 weeks' gestation. The mean number of SA visualized in a sagittal plane of the placenta increased from 8.83 ± 2.37 in the first trimester to 16.99 ± 3.31 in the late-third trimester. The mean SA-PI was 0.57 ± 0.12 in the first trimester and decreased progressively during the second trimester, reaching a nadir of 0.40 ± 0.10 at 24-25 weeks, and remaining constant until the end of pregnancy. SA-PSV was highest in early pregnancy with a mean of 57.16 ± 14.84 cm/s at 12-13 weeks' gestation, declined to a mean of 49.38 ± 17.88 cm/s at 20-21 weeks' gestation and continued to trend downward for the remainder of pregnancy, reaching a nadir of 34.50 ± 15.08 cm/s at 36-37 weeks' gestation. A statistically significant correlation was noted between SA-PI and UtA-PI (r = 0.5633; P < 0.001). Multilevel regression models with natural cubic splines were used to create reference ranges of SA-PSV and SA-PI for given gestational ages.
Conclusion: From early gestation, we have demonstrated the ability to image and quantify SA blood flow in normal pregnancy, and have developed reference ranges for use at various gestational ages throughout pregnancy. © 2023 The Authors. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Keywords: Doppler; placenta; spiral artery; superb microvascular imaging; uterine artery.
© 2023 The Authors. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal assessment of intravillous arterioles in normal pregnancy using superb microvascular imaging.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Jul 29:10.1002/uog.29308. doi: 10.1002/uog.29308. Online ahead of print. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 40726352
-
Ophthalmic artery Doppler in combination with other biomarkers in prediction of pre-eclampsia at 19-23 weeks' gestation.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jan;57(1):75-83. doi: 10.1002/uog.23528. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33142353
-
Reference ranges of uterine artery pulsatility index from first to third trimester based on serial Doppler measurements: longitudinal cohort study.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Apr;61(4):474-480. doi: 10.1002/uog.26092. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36206548
-
Maternal kidney function during pregnancy: systematic review and meta-analysis.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Sep;54(3):297-307. doi: 10.1002/uog.20137. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 30288811 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of the Placenta.Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Mar 1;68(1):72-85. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000905. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 39846881 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal associations between urinary biomarkers of phthalates and replacements with novel in vivo measures of placental health.Hum Reprod. 2024 Sep 1;39(9):2104-2114. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae152. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38970902 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal assessment of intravillous arterioles in normal pregnancy using superb microvascular imaging.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Jul 29:10.1002/uog.29308. doi: 10.1002/uog.29308. Online ahead of print. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 40726352
-
B-flow/spatiotemporal image correlation M-mode ultrasound provides novel method to quantify spiral artery remodeling during normal human pregnancy.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Sep;64(3):322-329. doi: 10.1002/uog.27636. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38477161
References
-
- Lyall F, Robson SC, Bulmer JN. Spiral artery remodeling and trophoblast invasion in preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction: relationship to clinical outcome . Hypertension. 2013;62(6):1046–1054. - PubMed
-
- Gebb J, Dar P. Colour Doppler ultrasound of spiral artery blood flow in the prediction of pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25(3):355–366. - PubMed
-
- Collins SL, Birks JS, Stevenson GN, Papageorghiou AT, Noble JA, Impey L. Measurement of spiral artery jets: general principles and differences observed in small-for-gestational-age pregnancies . Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2012;40(2):171–178. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous