Structure-Activity Assessment and In-Depth Analysis of Biased Agonism in a Set of Phenylalkylamine 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
- PMID: 37474114
- PMCID: PMC10401645
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00267
Structure-Activity Assessment and In-Depth Analysis of Biased Agonism in a Set of Phenylalkylamine 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
Abstract
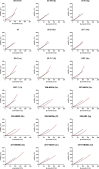
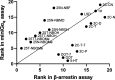
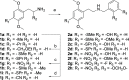
Serotonergic psychedelics are described to have activation of the serotonin 2A receptor (5-HT2A) as their main pharmacological action. Despite their relevance, the molecular mechanisms underlying the psychedelic effects induced by certain 5-HT2A agonists remain elusive. One of the proposed hypotheses is the occurrence of biased agonism, defined as the preferential activation of certain signaling pathways over others. This study comparatively monitored the efficiency of a diverse panel of 4-position-substituted (and N-benzyl-derived) phenylalkylamines to induce recruitment of β-arrestin2 (βarr2) or miniGαq to the 5-HT2A, allowing us to assess structure-activity relationships and biased agonism. All test compounds exhibited agonist properties with a relatively large range of both EC50 and Emax values. Interestingly, the lipophilicity of the 2C-X phenethylamines was correlated with their efficacy in both assays but yielded a stronger correlation in the miniGαq- than in the βarr2-assay. Molecular docking suggested that accommodation of the 4-substituent of the 2C-X analogues in a hydrophobic pocket between transmembrane helices 4 and 5 of 5-HT2A may contribute to this differential effect. Aside from previously used standard conditions (lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) as a reference agonist and a 2 h activation profile to assess a compound's activity), serotonin was included as a second reference agonist, and the compounds' activities were also assessed using the first 30 min of the activation profile. Under all assessed circumstances, the qualitative structure-activity relationships remained unchanged. Furthermore, the use of two reference agonists allowed for the estimation of both "benchmark bias" (relative to LSD) and "physiology bias" (relative to serotonin).
Keywords: 5-HT2A; biased agonism; in vitro pharmacology; miniGαq; psychedelics; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.E.G. is a part-time employee and warrant holder of Kvantify.
Figures
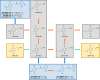
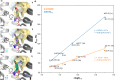
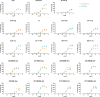
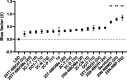
Similar articles
-
Discovery of β-Arrestin-Biased 25CN-NBOH-Derived 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists.J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 22;65(18):12031-12043. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00702. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36099411 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of psychedelic new psychoactive substances (NPS) showing biased agonism at the 5-HT2AR through simultaneous use of β-arrestin 2 and miniGαq bioassays.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;182:114251. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114251. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32998000
-
Pharmacological Mechanism of the Non-hallucinogenic 5-HT2A Agonist Ariadne and Analogs.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;14(1):119-135. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00597. Epub 2022 Dec 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36521179 Free PMC article.
-
Hallucinogens and Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathways.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:45-73. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_478. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28677096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemistry and Structure-Activity Relationships of Psychedelics.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:1-43. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_475. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28401524 Review.
Cited by
-
Psilocybin as Transformative Fast-Acting Antidepressant: Pharmacological Properties and Molecular Mechanisms.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;39(4):e70038. doi: 10.1111/fcp.70038. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40670864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of β-Arrestin-Biased 25CN-NBOH-Derived 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists.J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 22;65(18):12031-12043. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00702. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36099411 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Characterization of a Tryptamine-Based Visible-Light Photoswitchable 5-HT2AR Ligand Showing Efficacy Preference for β-Arrestin over Mini-Gq.J Med Chem. 2025 Jul 10;68(13):13628-13639. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00442. Epub 2025 Jun 18. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40532050
-
Comparative Pharmacological Effects of Lisuride and Lysergic Acid Diethylamide Revisited.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Feb 5;7(3):641-653. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00192. eCollection 2024 Mar 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481684 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanistic divide in psychedelic neuroscience: An unbridgeable gap?Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Mar;21(2):e00322. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00322. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 38278658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes N. M.; Ahern G. P.; Becamel C.; Bockaert J.; Camilleri M.; Chaumont-Dubel S.; Claeysen S.; Cunningham K. A.; Fone K. C.; Gershon M.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 310–520. 10.1124/pr.118.015552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

