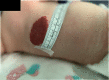
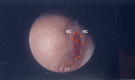
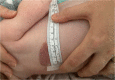
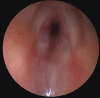
Upper airway infantile haemangioma presenting with an atypical synchronous skin lesion
- PMID: 37474145
- PMCID: PMC10357665
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2023-255223
Upper airway infantile haemangioma presenting with an atypical synchronous skin lesion
Keywords: Dermatology; Ear, nose and throat/otolaryngology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
