Adolescent childbirth and mobility disability among women ages 15-49: an analysis of population health surveys from 14 low-income and middle-income countries
- PMID: 37474178
- PMCID: PMC10360427
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072535
Adolescent childbirth and mobility disability among women ages 15-49: an analysis of population health surveys from 14 low-income and middle-income countries
Abstract
Objectives: Adolescent childbirth is associated with older adult adverse health outcomes that negatively affect mobility function, but these associations have not been studied globally in large samples of reproductive-age women. This study examines the association between age at first childbirth and mobility disability in national surveys from low-income and middle-income countries, and hypotheses that adolescent childbirth is associated with mobility disability.
Design: Cross-sectional analysis.
Setting: Population health surveys from 2013 to 2018 containing mobility disability measures among ever-pregnant women ages 15-49. These included 13 Demographic Health Surveys from Haiti, Pakistan, Uganda, Cambodia, Colombia, South Africa, Timor-Leste, Albania, Gambia, Maldives, Peru, Senegal and Yemen and 1 Maternal Health Survey from Ghana.
Participants: The sample included 157 988 women ages 15-49 years.
Primary outcome measure: Adolescent childbirth was defined as 10-19 years of age. Poisson regression models were used to estimate prevalence ratios (PRs) of mobility disability among women who first gave birth during adolescence and in adult life (ages 20-45 years) in each country and across the whole sample. Countries were also analysed according to the use of standard and non-standard mobility disability measures. Covariates included current age, urban/rural residence, education and household wealth.
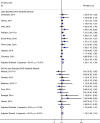
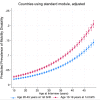
Results: Prevalence of adolescent childbirth (17.5%-66.2%) and mobility disability (0.32%-21.45%) varied widely across countries. Adolescent childbirth was significantly (p<0.05) associated with greater mobility disability in six of eight countries using standard disability measures. Among the six countries that did not use standard disability measures, none showed a statistically significant association between adolescent childbirth and mobility disability. Considering the whole sample and adjusting for all covariates, women who gave birth during adolescence had greater prevalence of mobility disability (pooled PR 1.19, 95% CI 1.06-1.31).
Conclusions: This analysis suggests a moderate and consistent association of adolescent childbearing with subsequent mobility disability.
Keywords: EPIDEMIOLOGIC STUDIES; Epidemiology; Public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . World report on disability; 2011. Available: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241564182 [Accessed 1 May 2023]. - PubMed
-
- World Health Assembly 58 . Disability, including prevention, management and rehabilitation. World Health Organization; 2005. Available: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/20373 [Accessed 1 May 2023].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
