Systems pharmacology dissection of pharmacological mechanisms of Xiaochaihu decoction against human coronavirus
- PMID: 37475019
- PMCID: PMC10357659
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04024-6
Systems pharmacology dissection of pharmacological mechanisms of Xiaochaihu decoction against human coronavirus
Abstract
Background: Although coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is still rage worldwide, there are still very limited treatments for human coronaviruses (HCoVs) infections. Xiaochahu decoction (XCHD), which is one of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions in Qingfeipaidu decoction (QFPDD), is widely used for COVID-19 treatment in China and able to relieve the symptoms of fever, fatigue, anorexia, and sore throat. To explore the role and mechanisms of XCHD against HCoVs, we presented an integrated systems pharmacology framework in this study.
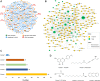
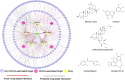
Methods: We constructed a global herb-compound-target (H-C-T) network of XCHD against HCoVs. Multi-level systems pharmacology analyses were conducted to highlight the key XCHD-regulated proteins, and reveal multiple HCoVs relevant biological functions affected by XCHD. We further utilized network-based prediction, drug-likeness analysis, combining with literature investigations to uncover the key ani-HCoV constituents in XCHD, whose effects on anit-HCoV-229E virus were validated using cytopathic effect (CPE) assay. Finally, we proposed potential molecular mechanisms of these compounds against HCoVs via subnetwork analysis.
Results: Based on the systems pharmacology framework, we identified 161 XCHD-derived compounds interacting with 37 HCoV-associated proteins. An integrated pathway analysis revealed that the mechanism of XCHD against HCoVs is related to TLR signaling pathway, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, cytoplasmic DNA sensing pathway, and IL-6/STAT3 pro-inflammatory signaling pathway. Five compounds from XCHD, including betulinic acid, chrysin, isoliquiritigenin, schisandrin B, and (20R)-Ginsenoside Rh1 exerted inhibitory activity against HCoV-229E virus in Huh7 cells using in vitro CPE assay.
Conclusion: Our work presented a comprehensive systems pharmacology approach to identify the effective molecules and explore the molecular mechanism of XCHD against HCoVs.
Keywords: HCoV-229E virus; Human coronavirus; Molecular mechanism; Systems pharmacology; Xiaochaihu decoction.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

